
Whether you're just starting your SEO journey or are a seasoned professional, you can count on one certainty: The landscape of SEO is ever-changing. If you're looking for a field where you can learn all the "right" strategies and then use them predictably and repeatedly forever, you're in the wrong place.
If, however, your brain lights up at the prospect of continually solving puzzles and adapting to advancements in the fascinating trajectory of search engine evolution, then read on and let's talk about NLP and how to find NLP keywords for SEO, one of the more complex facets of search engine optimization.
Since effective SEO always involves a combination of multiple approaches, some strategies are more straightforward than others. Maintaining a clean backlink profile, for instance, is something reasonably cut and dried. Using NLP techniques to your advantage, on the other hand, requires a fair bit of background knowledge, research, and intuition in understanding human language. Fortunately, there are also some excellent tools available to help you along the way.
My name is Terry Williams and I have been doing SEO a top agency for close to 5 years, specializing in NLP keyword research. In this post, I'll try to give you a solid understanding of some of the basics of NLP SEO so that you can begin integrating NLP strategies into your own SEO framework.
What Does NLP Stand For & What Is It?
NLP stands for Natural Language Processing, the research field focusing on transforming natural language into machine-computable information.
Linguistic AI capabilities have been rapidly advancing since the advent of search engine technology, and what would have seemed groundbreaking even just a few years ago is already obsolete. Gone are the days when Google worked with statistical models built around keywords. Today, NLP technology is focused on refining machine learning models to understand and dissect human language in increasingly sophisticated and comprehensive ways.
NLP takes the less tangible elements of text—such as tone, purpose, intent, and context—under close scrutiny and attempts to deconstruct them using powerful algorithms. The end goal, of course, is to find the magic formula that mimics the human mind as closely as possible—with all the power of artificial intelligence behind it.
Indeed, it sounds a bit like sci-fi. But the truth is that the more Google's algorithms understand human language, the more successful Google will be.
The BERT Update
At the end of 2019, Google announced the official BERT algorithm release. BERT (which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) was a game-changer in the SEO world because it was focused on quality content, context, and natural language processing. Since then, search engine optimization strategies have had to evolve to reflect BERT's criteria.
The Primary Goal of Search Engines
Before getting into how BERT changed SEO, it's important to understand the primary goal of search engines like Google.
To quote Milosz Krasinsksi from Oncrawl, "The best way to understand NLP from an SEO perspective is to first understand BERT. [...] BERT contains two major components: Data (pre-trained models) and methodology (defined ways to learn and use those models). [...] BERT collects specific sets of data relating to content and then learns how to analyze that data. NLP is BERT's brain. It's able to understand the word or phrase in its context by looking at various signals around it."
The signals Krasinsksi is referring to include, but are not limited to: The words directly preceding and following a particular keyword; subsections of pages as well as entire pages; and sentences, paragraphs, and queries as a whole.
As you can imagine, this NLP is different and drastically more nuanced than older algorithm models, which were more simply focused on keywords alone. Google is no longer so invested in isolated keywords. Rather, it’s looking to pinpoint tone, intent, and sentiment in context.
How Does Google Use NLP Keywords?
To be fair, whole generations of people have now grown up relying on Google (and other search engines) to meet their daily needs. The Google users of today are less patient and more exacting than their counterparts from a decade ago, and Google has to keep evolving to meet the demands of more complex queries and higher search engine expectations from the public.
In the end, it all boils down to the search quality that Google can yield.
As a result, Google is working extremely hard to understand the intent and context of search queries and web content. In other words, to understand natural language.
Using NLP, BERT measures sentiment. That's right. The Google algorithm scores texts to determine whether they’re positive, negative, or neutral. Positive sentiment is scored between 0.25 and 1, while negative sentiment is given a value between -0.25 and -1. Neutral sentiment falls in the numerical range between -0.25 and 0.25.
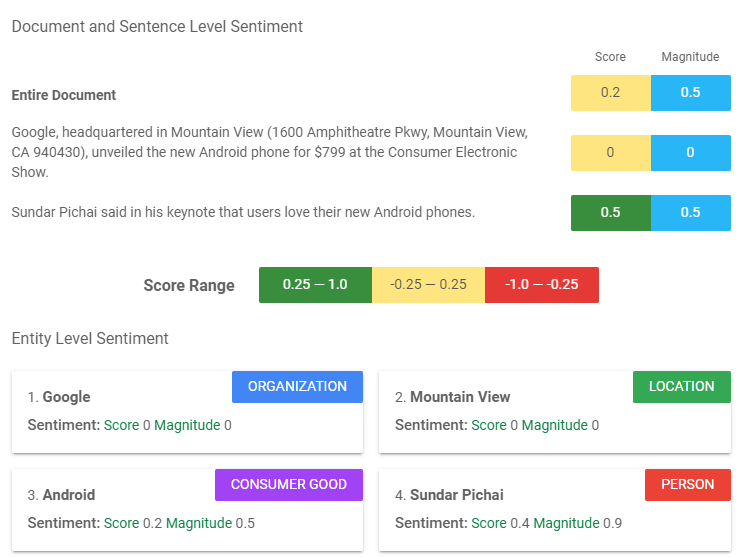
From an SEO perspective, this is significant because if BERT has scored all your highest-ranking competitors' pages as positive (i.e., their pages contain positive words and phrases), then your page had best be positive, too in order to compete. Obviously, this is a little over-simplified, but it essentially illustrates the SEO power that can be harnessed by understanding sentiment, as defined by BERT.
Are NLP Keywords a Ranking Factor?
Yes. NLP keywords are a ranking factor. They’re only one piece of the SEO puzzle, but they can definitely have the traction to move your rankings in the right direction.
NLP essentially interprets BERT's metrics to help Google understand what makes better content. If you can optimize your content accordingly, you'll reap the rewards in higher rankings. All other factors being equal, if you can directly compare your page to the top-ranking pages and optimize your content to reflect the same NLP keywords, then you should be able to rank highly too. Of course, you'll also need to take factors such as context and sentiment analysis into consideration.
NLP Vs. LSI Keywords
Alright, before we move on to specific strategies, let's clarify one more concept: LSI keywords.
LSI (latent semantic indexing) is something of a contentious term in the SEO industry. Often used loosely to mean almost any technology used for the purpose of semantic analysis, LSI is actually one specific implementation of language processing. Technically, it falls under the broader umbrella of NLP.
Developed in the 1980s, LSI focuses on AI learning a wide variety of synonyms based on context. It uses mathematical techniques to find relationships between words.
The contention largely stems from people using the term LSI incorrectly. While some SEO trend-setters do still refer to LSI as an important ranking factor, most feel that it’s outdated and effectively replaced by Google's more modern NLP.
Either way, the fact remains that semantic analysis remains an important factor in the search optimization world.
Understanding Entities in SEO
Let's take a moment to understand the term entity. As defined by Google, an entity is anything that’s "singular, unique, well-defined, and distinguishable". Like a noun, an entity is often physically tangible but doesn't have to be. It could be something abstract, like an idea, relationship, or historical event.
Entity-based SEO builds on search engines' attempts to generate the most accurate results by connecting user intent, context, and the relationship between words. In practice, this means that search results are often generated based on words or phrases that are connected to a particular entity—but that doesn't specifically name it (sometimes known as identifiers).
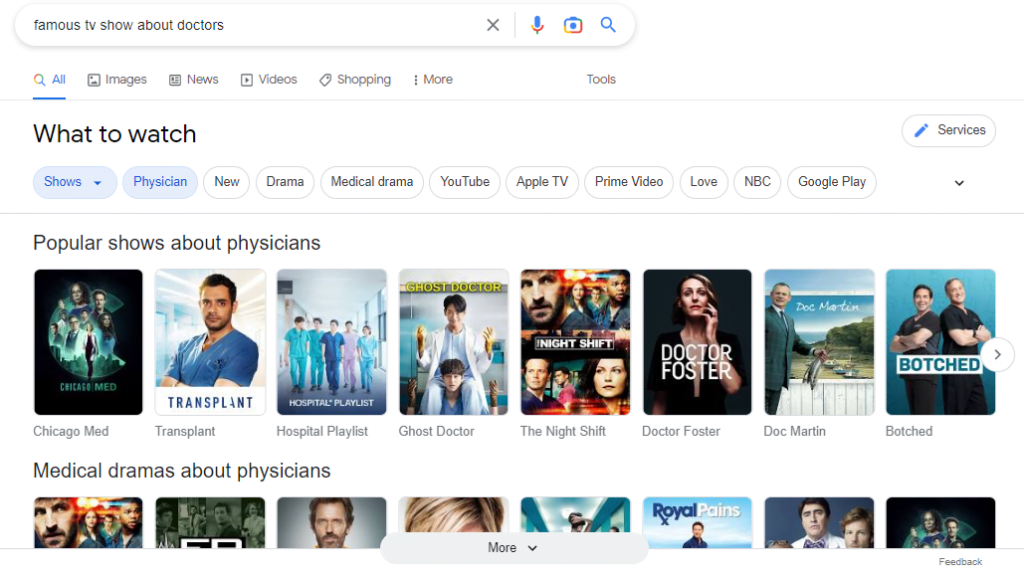
For example, if you type "famous tv show about doctors" into Google search, you'll come up with a list of TV shows that include doctors in them. In this case, these show titles are the entities, but the search engine has used NLP technology to identify a word or phrase directly related to the subject.
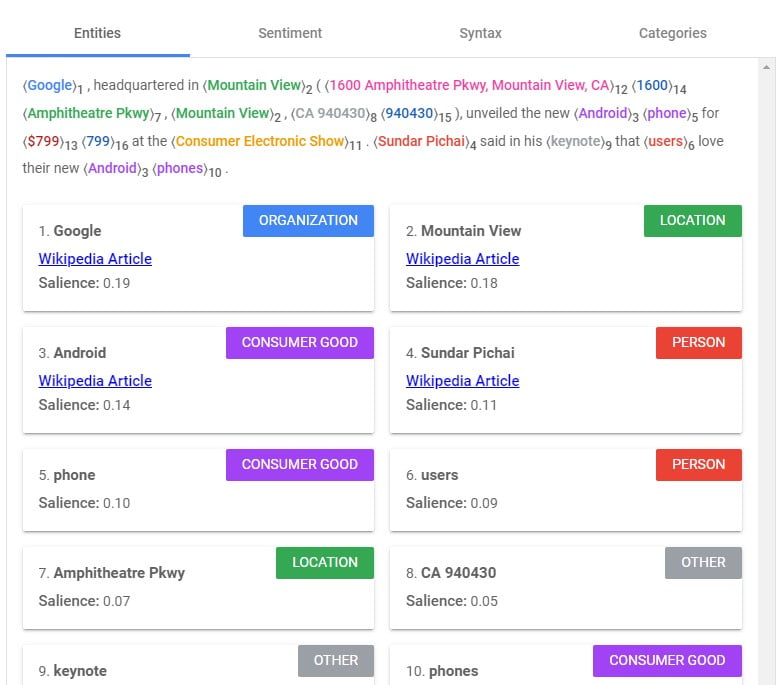
Google's NLP picks up on words related to entities in fairly subtle ways, including salience—their relevance or importance in a particular text—and ranks them in order of importance to the context of the page. Like sentiment analysis, saliency analysis is recorded numerically. It ranges from 0.0 for no saliency up to 1.0 for highly salient identifiers. Entities are also ranked by category, which is a more familiar concept for those in the SEO trenches.
Entities mark a shift away from keywords as the primary focus behind Google searches. Using NLP, Google is aiming to build contextual connections and minimize ambiguity to improve the quality of its search results.
As an example, if someone types a single keyword search such as "banana" into a search engine, it’s impossible to know whether their intent is to find out about the vitamins in bananas, banana recipes, or banana plants. A search such as, "fruits high in potassium", however, might turn up a wealth of relevant information about the health benefits of bananas—if Google's NLP can pick up on the intent behind the query.
Mobile searches and voice searches through digital assistants are also much easier with entity SEO. At SerpFocus, we believe it’s important to recognize this trend and use it to leverage your own SEO.
How Do I Identify NLP Keywords To Use in My Content?
As I mentioned at the beginning of this post, there are some great tools that can really help you to optimize your content using NLP keywords. Thank goodness!
One is Google's Natural Language API. This API is a comprehensive tool that carries out entity analysis, sentiment analysis, content classification, multi-lingual analysis, plus more. It allows you to plug into and examine any text, providing you with valuable NLP data. Not only can you transparently see how Google has analyzed your content, but you can also see how it has analyzed the content of high-ranking pages in your niche.
How to Use Google Natural Language API Tool to Optimize Your Content
Step 1: Find the Right Keyword
Targeting the right keyword is critical for creating optimized, high-ranking content. Google's Natural Language Processing (NLP) API can analyze keyword difficulty, search volume, and intent to identify the best terms to focus your content around.
Follow these steps to leverage SEMrush for better keyword targeting:
- Identify a preliminary seed keyword that encapsulates your topic using Google's Keyword Planner or keyword research tools like SEMrush.
- Take your preliminary keyword and input it into the SEMrush's keyword explorer. This analyzes the keyword for attributes like search volume, competitiveness, and user intent.
- Review the results to narrow down more specific long-tail variants that reveal high volume search intent while remaining less competitive. For example, "buy iPhone X on installments" indicates commercial intent vs just "iPhone."
- Compare long-tail keywords against tools like Google Trends to verify demand and seasonality. This ensures you target keywords aligned with real user searches.
- Select keywords that clearly communicate user intent - whether informational, commercial transactional, or navigational - so you can satisfy the search purpose.
- Avoid generic, short-tail keywords that lack clear intent signaling, as targeting the wrong intent leads to poor engagement and clicks.
- Focus on long-tail keywords with sufficient search volume for your niche, generally at least 100+ monthly searches.
- Double check relevance to your offerings to align with user expectations..
By leveraging tools like SEMrush and Google Trends, you can optimize around keyword difficulty, search volume, seasonality, and intent. This ensures you provide the most relevant content to rank highly and fulfill searcher needs.
Step 2: Review the Top Ranking Websites
While never advisable to duplicate or plagiarize content, examining top results provides useful optimization insights. Specifically, the Natural Language API can extract key semantics, topics, entities and syntax from high-performing content.
To leverage these capabilities:
- Search your target keyword and identify the top 3-5 ranking pages in Google's results.
- Copy the full raw text content of each top result page. This is only for analysis, not replication.
- Paste the raw text into the Natural Language API explorer tool. Make sure to analyze each top result page separately.
- Review the API's analysis detailing content topics, keywords, entities, sentiment, syntax complexity and more.
- Make note of common themes around topics covered, semantic connections between concepts, formatting approaches, reading ease, entities mentioned.
- Use these insights to shape your own content for optimal relevance and engagement by aligning with practices of proven pages, without directly copying.
The Natural Language API uncovers the elements driving success for existing pages. This allows you to emulate high-performing content without duplication. The knowledge transfers into creating content refined for your topic and audience while satisfying Google's key ranking factors.
Step 3: Using the Google Natural Language Tool
The Google Natural Language API provides powerful linguistic analysis to extract key information from text content. Using the API can provide optimization insights by examining top ranking pages.
Running analysis you've done in the previous step generates results in four main categories:
- Entities - The API detects and tags all entities mentioned, which are defined as distinct concepts and real-world objects like people, organizations, locations, etc. Identifying key entities can indicate useful topics and semantics.
- Sentiment - Sentences are classified as conveying positive, negative or neutral sentiment. This reveals the overall tonal balance and emotion of the content.
- Syntax - The API analyzes the syntactic structure and grammar complexity of sentences. Reviewing syntax patterns can help shape clear, readable content.
- Categories - Content is algorithmically categorized into overall topics and subject matter based on keywords, entities and meaning. Useful for optimizing topical relevance.
These categories provide data to derive key elements leading to the content's high performance - semantic focus, readability, sentiment, entities and more.
Without duplication, you can mold your own content to better incorporate successful elements and align with qualities that resonate with search engines and users. The API exposes building blocks to engineer optimized content without copying.
Step 4: Google Sheet Work
After running text through the Natural Language API, the next step is transferring the output to Google Sheets for further analysis. This allows you to easily parse the data for key optimization insights.
To leverage Google Sheets:
- Copy the API output and paste it into a Sheet organized by categories - entities, sentiment, syntax, and categories.
- Within the entities output, highlight words and phrases that appear most relevant to the niche based on frequency and context. These represent important semantics.
- For lower competition niches, also note less common entities with higher "salience" scores as these may represent untapped opportunities.
- In the sentiment analysis, make note of strongly positive and negative sentences to identify emotional triggers to either amplify or avoid.
- Evaluate syntax patterns from the API like sentence length, grammar complexity, and common terms to shape readable content.
- Verify the API-detected content categories match your target niche. If not, adjust terminology in your content to better convey topical relevance.
- Use Sheets' filtering and sorting to surface key data like frequently occurring entities, high salience terms, positive sentiment sentences, and relevant categories.
The goal is transferring Natural Language API data into actionable insights without directly replicating content. Sheets provides a workflow to easily analyze results and derive optimization opportunities for your unique needs.
Step 4: Optimizing Content Based On This Data
Analyzing top-ranking content with Google's Natural Language API provides invaluable data to optimize your own content without duplication. Here are key optimization steps:
- Identify Intent
Examine what types of results Google shows for your keyword - images, lists, videos, etc. Then craft content aligned with that dominant intent. Match the type of content searchers expect. For example if you search 'seo tips' in Google and it shows a list, perhaps you need a list in your content.
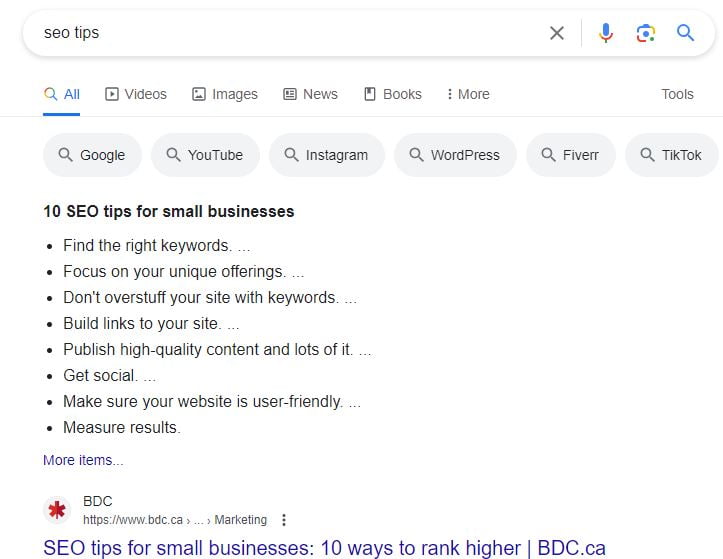
If you search something like "link whisper tutorial' and video rich snippets are displayed, you would want to consider creating a Youtube video and embedding it onto your page.
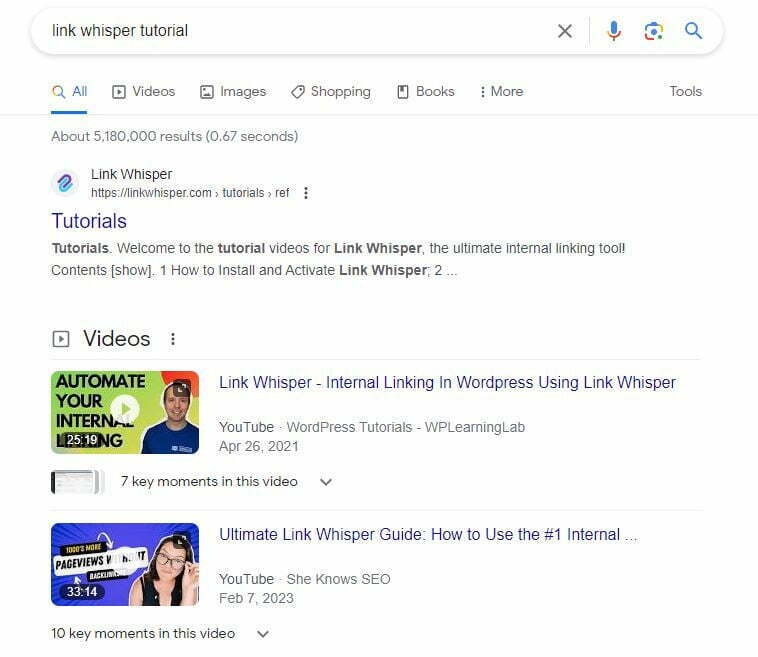
Lastly, if a keyword you were analyzing was 'lenovo laptop' you would notice product rich snippets like this:
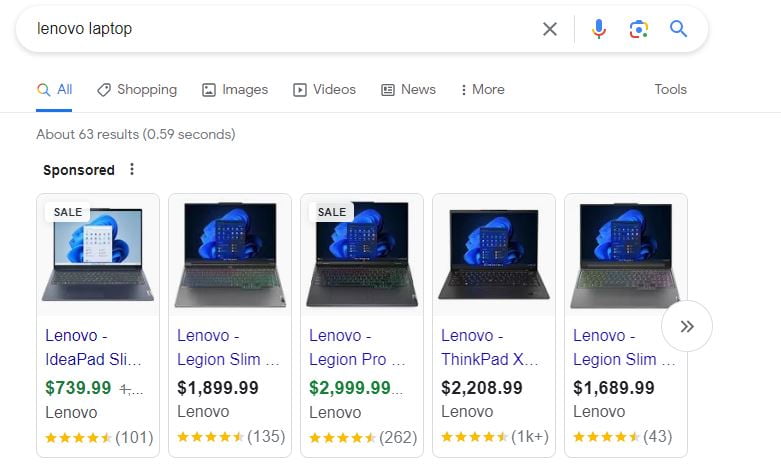
So if you were trying to rank for that keyword, Google expects to see a product page. If you are not actually selling those laptops, it will be unlikely that you rank well for that keyword. This is what I mean when I saw your keyword should satisfy the user's search intent.
- Improve Page Speed
Fast page loading helps avoid "pogo sticking" where visitors quickly bounce back to the SERP. Optimizing speed with caching, image compression, efficient code and more leads to better engagement. Google has also confirmed that page speed is a ranking factor.
- Strategic Keyword Targeting
Incorporate keywords naturally in titles, headers, meta descriptions, content, alt text and URL. Vary word order for long tails. Avoid over-optimization. Refer to existing top results for guidance.
- Use Searcher-Friendly URLs
Create URLs with dashes between words instead of underscores or camelcase. Incorporate keywords where logical. This improves clickthroughs and sharability. Can you tell which URL would be easier for Google to understand?
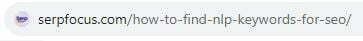
OR

- Optimize Image SEO
Add strong alt text to images to that accurately describe the image.
Expert Insight:
To optimize your image alt text, look to what is already working well in Google Image Search. Find relevant high-ranking images for your keyword and view their source code to analyze the alt text used.
This allows you to derive proven, effective image descriptions and keywords to model your own alt text after. The best practices are right there in the alt text of top images ranking on Google. Simply search your target keyword in Google Images, open the source code of a highly ranking result, and inspect the alt tag attributes for optimization ideas worth emulating.
- Exceed Competitor Content
Create more extensive, insightful and quality content than competitors. Answer related questions searchers have. Include supporting data and research. Format content for easy skimming. But what qualifies as quality content. John Mueller, a Google Search Relations Expert says "“With regards to quality content, in general this is something where you as the site owner probably know a lot more about what is actually quality content for your specific kind of site...you need to show that you really have something that’s unique and compelling and of high quality.”
Expert Insight:
Answer questions from Google's People Also Ask section
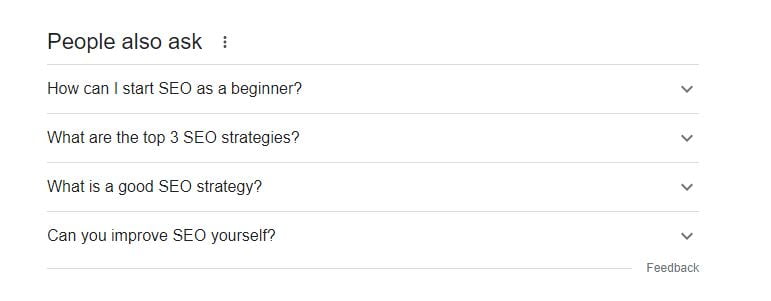
A little trick to get more questions is to click a question to expand that section, then click it again to close it. Google will generate more questions

- Incorporate Mixed Media
Use relevant images, graphics, videos, GIFs to boost engagement. Studies show most consume multi-media content over text alone. Can also aid memory and recall.
- Interlink Related Content
Strategic internal linking between related content can boost keyword rankings. This is because internal links allow PageRank equity to flow from older, established pages to newer ones, passing authority and relevance signals. Read our guide on improving keyword rankings with internal links to learn proven linking strategies.
- Bring It All Together
Blend optimized technical components with compelling, information-rich content. Every element should provide value. Avoid bloated length without purpose. Create a positive user experience.
Following these optimization best practices unlocks the full potential of your content based on an analytical approach using Google's NLP API. The combination of scientific linguistic analysis with strategic optimization results in pages built to satisfy both search engines and searchers.
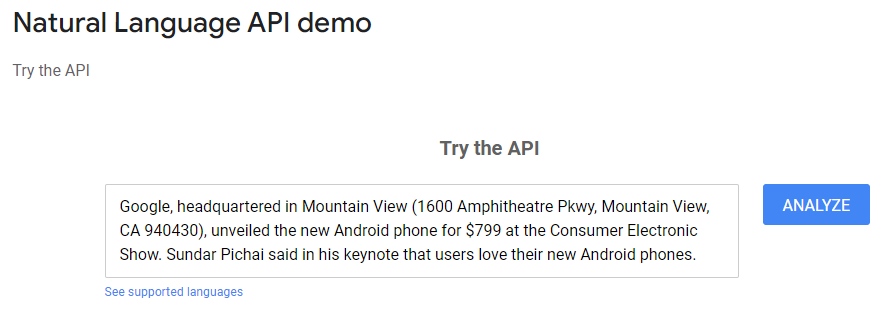
Alternative to Using Google's Natural Language Processor
Using Surfer SEO
Surfer is probably the gold standard when it comes to identifying specific NLP keywords to optimize your content. By linking to Google's NLP API, Surfer provides users with the words, phrases, and sentiments that Google has identified as significant in relation to any given entity. It also analyzes top-ranking pages so you can see how often you should be using various NLP entities and identifiers in your content. This is an incredible feature and takes so much of the guesswork out of NLP SEO! Read my Surfer SEO review here.
Using the Concept of TF-IDF and TextRank
Natural language processing leverages some core algorithms to extract the most meaningful keywords within a document or passage of text. Two of the most common methods are TF-IDF and TextRank.
TF-IDF
Short for term frequency–inverse document frequency, TF-IDF analyzes how frequently a term appears within a document while adjusting for how common that term is across all documents.
It calculates a score for each word based on:
- Term Frequency (TF) - The number of times the term appears in the document. More frequent tends to mean more relevant.
- Inverse Document Frequency (IDF) - The log of the number of documents divided by the number of documents containing that word. This lowers the score of common words like "the" that appear across documents.
Words with the highest TF-IDF scores are deemed the most relevant keywords for a document since they contain a high term frequency within that specific document but a low document frequency overall.
TextRank
TextRank is based on an algorithm similar to Google's PageRank, but it analyzes the "votes" between words in a document to determine which are most central to the content.
It builds a connectivity graph between words, where each word represents a node. When words co-occur closely in sentences, they "vote" for each other with a link. The score of a word is based on the number and scores of words voting for it.
This identifies topically significant words within the graph based on the concept that densely interconnected nodes likely belong to the core topic. Words linked together form natural communities reflecting key concepts.
TextRank and TF-IDF can be used together, with TextRank helping cluster semantically related words and TF-IDF scoring them by relevance. For NLP keyword analysis, these fundamental techniques provide the computational foundations.
Tools to Implement TF-IDF Keyword Extraction Automatically
- sklearn - The scikit-learn Python library contains TF-IDF implementations like TfidfVectorizer and CountVectorizer that can be used for keyword analysis.
- NLTK - The Natural Language Toolkit for Python has TF-IDF functions like tfidf_model() and basic tokenization.
- spaCy - spaCy is an advanced NLP library for Python with detailed docs on applying TF-IDF.
- TextBlob - TextBlob is a Python NLP library built on top of NLTK that provides a simple TF-IDF interface.
- RapidMiner - Data science platform with drag-and-drop TF-IDF operators and workflows.
- Apache OpenNLP - Java library for NLP with TF-IDF capabilities.
The easiest way to implement TF-IDF is leveraging a pre-built library like sklearn or NLTK in Python. But many data science tools across languages contain TF-IDF capabilities ready to apply out-of-the-box.
Are There Any Risks With Implementing NLP into Your SEO Strategy?
As with any new endeavor, the biggest risk of implementing NLP into your SEO strategy is not doing proper research. But done right, I can only see NLP SEO benefitting you and your business.
While more traditional ranking factors remain highly valuable, the truth is that Google is embracing user intent and search relevancy in a major way...which means that those of us in the SEO industry probably should be as well.
Jumping into NLP SEO may feel intimidating, but if you can be one of the earlier birds to get in on this trend, it could have substantial rewards! My advice is definitely to add it to your toolkit asap. I don't believe NLP is on its way out. To the contrary, I believe it will only continue to evolve and gain momentum.
Other Use-Cases
To finish off this post, let's take a look at some specific examples of how you can leverage NLP to your advantage as a business owner. As we know, there's no silver bullet in SEO. But a combination of these strategies could be a great starting point for refining your approach to NLP SEO.
Structured Data Markup Automation
Structured data markup is a machine-readable representation of your product data directly on your site. By extracting entities and their unique identifiers, you can optimize your structured data markup for NLP. This is called structured data markup automation and will help search engines index your website more effectively.
Mega-sites like BBC, Reuters, and Eventbrite are employing this strategy to increase visitors to their web pages with great success. Why not use it yourself?
Internal Linking
We all know about the importance of backlinks (external links) in SEO. But, with the advent of NLP SEO, internal linking has also become a major—and impactful—focus. While authority and relevance remain important factors for effective link-building, context, link structure, and placement have also joined them in the front seat.
Internal links serve a few purposes. They help users discover content from your website, they improve user experience and the length of time new visitors spend on your site, and they help search engines evaluate your content and whether the user experience it provides is effective or not. A strong, logical internal linking structure significantly helps your SEO. There are tools that assist you with the internal linking process, for example read my review on Link Whisper.
To maximize your in-link building, you can extract the entities from your content and then create (and internally link to) more content based around them. This can be an opportunity for you to increase the organic content on your page while also expanding on concepts in-house that visitors might previously have had to leave your page to find. For example, you might decide to add an introduction to a topic, some definitions, or further information about a relevant entity.
This sort of content bolstering can be a win-win-win. If you pull it off well, it allows you to expand and improve your website (with more links and more information), keeps visitors engaged longer, and is also a savvy NLP strategy for boosting your Google rankings.
Content Recommendation
Content recommendation is the practice of using machine learning algorithms to predict what a user might like to read next. Done right, it can dramatically increase the number of time visitors spend engaged on your website—and, thus, your rankings.
NLP can inform machine learning models that help users jump from one engaging article to the next. This intersection between NLP and machine learning (among other elements) is known as Semantic AI. If you’re interested in seriously integrating Semantic AI into your SEO strategy, SerpFocus recommends checking out the PoolParty platform. PoolParty is an award-winning Semantic AI platform designed to help you build smart applications and systems.
Conclusion
If you've made it here to the end with me, I hope this post has been helpful. NLP is a complex topic, but one very worth delving deeper into if you really want to get to the core of how search engines are evolving—and how SEO is evolving as a result.
Understanding NLP gives you more insight into how your page looks through Google's eyes. Like anything, its power can be harnessed to your advantage. But you have to take the time to do proper research and optimize your content accordingly in smart and relevant ways.
In this post, I've covered some basic concepts about NLP SEO, but they're only intended as jumping-off points for you to explore further, research, and experiment with. We'd love to hear more about your experiences with NLP-based SEO strategies.
Let us know about your successes, challenges, and—especially—your questions. At SerpFocus, our aim is to provide SEO and marketing support, so don't hesitate to reach out, no matter where you're at in your SEO journey.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.