Search engine optimization (SEO) refers to the process of improving a website's visibility and rankings in search engines like Google. A key component of effective SEO is optimizing your site according to the major ranking factors search algorithms use to assess pages.
SEO ranking factors refer specifically to the elements and signals that search engines evaluate when determining where to rank pages in results for a given search query. The most significant factors have a direct correlation to higher rankings for target keywords, so optimizing them should be a priority.
Mastering both the foundational and advanced list of ranking factors is crucial for success with organic search. A few reasons why optimizing for known ranking factors should be central to your SEO efforts:
- Helps maximize your chances for high rankings against competitive keywords. The better you satisfy what search engines are looking for, the higher you can rank.
- Provides proven direction on what you should focus your time and resources on for SEO.
- Allows you to diagnose issues weighing down your rankings and correct them.
- Keeps your site aligned with constant search algorithm updates over time.
This post will provide a comprehensive overview of the most influential SEO ranking factors across categories like on-page, technical, and local SEO. Understanding these key elements that impact rankings will give you a blueprint for optimizing your website and content to achieve higher organic visibility.
What Does Google Look for in SEO?
Google processes over 3.5 billion searches per day, so delivering fast, accurate, and relevant results is essential to their mission of organizing the world's information. To achieve this, Google relies heavily on search engine optimization signals and factors when indexing pages and ranking results.
The process starts with Google's web crawlers, which continuously scan and index trillions of web pages across the internet. As these automated bots crawl each page, they analyze and catalog a variety of ranking signals and factors to assess the page's value and relevance.
Specifically, Google is evaluating elements like:
- The content on the page - Is it high-quality, unique, and provide value to searchers? Does it satisfy the query intent?
- The code and technical optimization - Is the site fast, secure, and mobile-friendly?
- The popularity and links - Does the page have authority based on incoming links and engagement?
- The user experience - Does the page easily inform and satisfy visitors?
Based on all these factors and more, Google determines a general relevance score for each page relative to individual searches. Its complex ranking algorithms then sort pages by these relevancy scores and additional weighting factors to decide the final SERP rankings.
The pages Google identifies as offering the best overall user experience, value, authority, and relevance for the search will earn the top spots. So optimizing for this wide range of ranking factors is key for any site owner.
Once your pages start appearing in results, good on-page SEO also helps get searchers to click your link through clear, compelling titles and meta descriptions. But earning those high rankings requires understanding exactly what Google wants to see on-page and off based on their core ranking factors and algorithms.
Top 10 Current SEO Ranking Factors for Google
1. A Secure and Accessible Website
One of the foundational technical SEO ranking factors is having a website that Google can easily crawl and index. If Google's bots encounter obstacles in discovering or accessing your pages, it directly damages your rankings potential.
Optimizing website accessibility involves:
- Using clean, semantic HTML code and a mobile-responsive site builder or theme. Sloppy code can confuse Google and hinder bots from crawling efficiently.
- Implementing an optimized robots.txt file that provides helpful instructions on what Google can and cannot crawl. This improves crawl efficiency.
- Creating and submitting an XML sitemap that lists all pages Google should index. Sitemaps function like a map to guide bots.
- Ensuring fast page speeds by optimizing images, enabling caching, and minimizing plugins. Slow load times frustrate users and hurt rankings.
- Making the website mobile-friendly and adapting content display for smaller screens. Over 50% of search traffic comes from mobile devices.
- Acquiring an SSL certificate and enabling HTTPS across the site. HTTP sites are slowly being phased out of search results.
- Eliminating broken links which create frustrating 404 errors. Fix or redirect any broken pages.
Satisfying these technical SEO factors demonstrates to Google your site is secure, user-friendly, and built to be crawled. While not direct ranking factors, foundational elements like optimized site architecture, clean code, and fast speeds establish trust and authority.
If bots struggle to access your site due to issues like complex navigation, slow speeds, or broken links, you have no chance of ranking well no matter how strong your content may be. Just as you need a sturdy foundation to build a house on, basic technical SEO forms the groundwork for all other optimization efforts.
By running a technical seo audit and addressing factors like site speed, mobile optimization, proper robots.txt files, and enabling HTTPS across the site, you demonstrate to Google your pages are ready to be indexed and surface in search results. This prepares the ground for higher rankings by avoiding technical pitfalls that hold many sites back.
2. Page Speed (Including Mobile Page Speed)
Page speed, particularly on mobile devices, has become one of the most crucial technical SEO ranking factors in recent years. With Google's algorithms placing more emphasis on user experience, sites with slow load times are being penalized in rankings.
The reasoning is that sites unable to quickly load and display content provide a poor user experience. Factors that determine page speed include:
- Minimized HTML, CSS, JavaScript and image files sizes
- Browser caching enabled
- Compressed image formats like WebP
- Minimal redirects
- Effective use of CDNs to distribute assets
- Minimal ads and trackers dragging down speed
- Fast, optimized web hosting service
- Lean, performant site architecture and code
In 2018, Google rolled out its Speed Update that specifically targets page speed on mobile devices. With over 50% of searches happening on smartphones, slow mobile load times negatively impact rankings.
Google recommends aiming for the following speeds:
- Mobile sites: < 3 seconds
- Desktop sites: < 5 seconds
Their testing tools like PageSpeed Insights and Mobile-Friendly Test can measure your real-world speeds and provide optimization tips. Monitoring speeds in Google Search Console can also reveal issues.
Optimizing page speed has become essential given its significance as a ranking factor. By improving load times, sites keep users happy while signaling technical competence to Google algorithms.
Even marginal speed improvements like compressing images, enabling caching, and removing heavy widgets can boost speeds that incrementally benefit rankings.
For WordPress sites especially, plugins like caching tools, image optimizers, and performance monitors are crucial to maximize speed as a key SEO signal.
3. Mobile Friendliness
With mobile internet usage now exceeding desktop usage globally, delivering an optimal experience on mobile devices has become imperative for SEO success. As a result, mobile-friendliness has emerged as a hugely influential ranking factor.
Google first confirmed that mobile-friendliness influences rankings in 2015 with the release of their Mobilegeddon update. Since then, the significance of mobile optimization has only grown, especially with the rising adoption of mobile-first indexing.
What exactly constitutes a "mobile-friendly" site in Google's eyes? Key elements include:
- A responsive design that automatically resizes and reflows content for smaller screens. Static desktop sites don't adapt.
- Tap-friendly navigation and menus suitable for touchscreens. This includes minimal menus requiring precise clicking.
- Avoiding small text that is hard to read on compact displays. Brief, skimmable content works best.
- Optimized apps for Android and iOS if one is offered. Native apps enhance the experience.
- Streamlined, fast-loading pages under 1-2 seconds on 3G connections or better. Speed is crucial.
- Eliminating interstitials, pop-ups and ads that clutter the screen or block access on mobile.
Satisfying these criteria ensures your site offers the ideal viewing and usage experience on smartphones and tablets. This signals to Google algorithms that you respect mobile users and have taken steps to accommodate their needs.
In contrast, sites that are overflowing with ads, have tiny text, require excessive scrolling or tapping, or aren't responsive convey neglect for the mobile audience. Given mobile is the future, such sites will struggle in rankings.
By making mobile optimization a priority, website owners can future-proof their presence while aligning with the mobile-first direction search is headed. Ensuring your site satisfies mobile-friendliness ranking factors demonstrates an understanding of modern users and technology.
4. Optimized Content
Creating high-quality, optimized content should be a central focus of any SEO strategy. The content itself on a page plays a major role in determining search rankings according to Google's algorithms. Satisfying the criteria for content optimization signals to Google that your pages offer value, expertise, and relevance worthy of a higher ranking.
Some key elements of optimized content as a ranking factor include:
Targeting Relevant Keywords - Conduct thorough keyword research to identify terms and phrases that are popular among your audience and have decent search volume. Incorporate these organically throughout your content to indicate topical relevance. Avoid keyword stuffing. Read our guide on the best tools to use for keyword research.
Using LSI Keywords - Sprinkle in latent semantic indexing (LSI) keywords and synonyms related to your core terms to provide further context. This helps Google understand the broader topic and meaning.
Matching Searcher Intent - Tailor your content's depth and focus to align with the intent behind keyword searches. Informational, transactional, and navigational searches each call for a different content approach.
Creating Unique, Original Content - Avoid thin or duplicate content by producing original, high-quality content not found elsewhere. Google rewards fresh, useful information.
Optimizing Length - Content over 2,000 words tends to perform better in search results. Long-form content is more authoritative and satisfies user intent for complex topics.
Formatting Content Clearly - Use headings, lists, images, videos, tables and other formatting to create scannable content. This enhances reader experience and engagement.
Incorporating Multimedia - Videos, images, infographics and other media boost engagement. Also provide alt-text and transcripts to optimize multimedia content.
The higher quality and more engaging your content is, the better chance it has of satisfying searchers' needs. This leads to higher click-through rates and lower bounce rates - metrics Google monitors closely.
Conversely, thin, low-value content padded with keywords fails to retain visitor attention. Poor user experience signals irrelevance to Google.
By providing truly useful, thoughtful information you compel visitors to not only click your listing, but stay, explore, and convert on your site. Over time, this builds authority and trust that Google recognizes through higher rankings.
So optimizing content for elements like searcher intent, length, multimedia use, and originality proves your pages deserve prominence in search results. Treat content creation as a crucial component of SEO rather than an afterthought. The effort can propel your rankings and traffic to new heights.
Fresh Content
The idea that frequently updating or publishing new content can improve Google search rankings has persisted as a myth among some in the SEO community. This seeming fixation on "content freshness" stems primarily from misconceptions around Google's major indexing updates like Caffeine and semantics around "Freshness Updates."
In reality, fresh content itself is not universally applied as a ranking factor. However, for certain searches where recency and new information is critical, freshness does play a role.
The roots of fresh content speculation trace back to Google's "Query Deserves Freshness" (QDF) initiative in 2007. This new algorithm tried to determine when searchers wanted the most recent information on a topic.
For trending news, regularly updated events, and other timely subjects, fresh and recent content is prioritized. But evergreen or non-time sensitive subjects do not require constant content updates to rank well.
Later, the Caffeine infrastructure update in 2009 focused solely on improving indexing speed and capacity - not rankings. Despite this, misinterpretations spread implying fresh content would be favored.
It wasn't until 2011 that an actual "Freshness Update" to Google's ranking algorithm rolled out. This aimed to better satisfy searches seeking the latest information on hot topics and current events.
But again, the update did not universally reward fresh content across all searches. As John Mueller clarified, constantly updating publication dates or content just to seem fresh is an ineffective SEO tactic.
In summary, while fresh content can benefit rankings for queries sensitive to recent information, it is not a general ranking factor. Google itself advises focusing on providing lasting value to users rather than playing games around content freshness.
For most sites, chasing freshness offers minimal ROI compared to investing in high-quality, evergreen content. The exceptions are sites producing content tied to trends and current events that evolves rapidly.
But for many niches, useful content does not go stale quickly. So modernizing publication dates or frequently rewriting existing content is unnecessary and inefficient. Google's core ranking systems reward overall usefulness, relevance and authority - not simply freshness.
5. Technical SEO
While quality content is essential for SEO success, how that content is technically structured and presented to search engines also significantly influences rankings. Optimizing the technical elements of your pages demonstrates an understanding of best practices and enhances the crawling and indexing process.
Some key technical SEO factors include:
- Page titles - The <title> tag is one of the most important elements that tells search engines and users what the page is about. Titles should be concise and include primary keywords.
- Header tags - Proper header structure using <H1> to <H6> tags helps indicate semantic hierarchy to search bots and improves on-page SEO.
- Meta descriptions - Well-written <meta> descriptions improve click-through rates by summarizing page content and enticing searchers.
- Image alt text - Concise, keyword-focused alt text for images enhances image SEO and improves accessibility.
- Structured data - Adding schema markup enables rich results and snippets to stand out in SERPs.
- Site speed - Faster page speeds improve user experience and are better for SEO. Minify code, enable caching, compress images, and optimize servers.
- Mobile-friendly - With mobile usage dominating, responsive mobile-friendly design is strongly favored by Google.
- Strong HTML - Well-formed HTML code aids crawling and prevents indexing issues that can negatively impact rankings.
- URL structure - User and SEO-friendly URLs improve click-through rates and ensure pages are properly crawled.
Though not as directly tied to relevance as content, satisfying these technical SEO factors demonstrates competence to Google. While users see the content, Google bots analyze how the site is built behind the scenes.
Tools like All in One SEO for WordPress make optimizing technical elements easy through its SEO title and meta description manager, XML sitemaps, schema markup features and more. Even non-technical users can leverage it to improve technical optimization to ultimately enhance search rankings.
Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals (CWV) refers to a set of metrics that quantify the user experience of a website in terms of loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability. The three core metrics are:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) - Measures time to load main content
- First Input Delay (FID) - Measures responsiveness to first user interaction
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) - Measures visual stability
In 2024, Interaction to Next Paint (INP) will replace FID as a core metric, measuring a site's overall responsiveness to user inputs.
Google has explicitly confirmed that Core Web Vitals are used as ranking signals. Faster, more visually stable sites with better interactivity tend to rank better. However, relevance remains the dominant factor - a slower but highly relevant page can still outrank a faster, less relevant page.
While improving CWV can benefit rankings, it does not guarantee moving up in results. Google evaluates overall user experience holistically, not just based on changes in specific metrics.
But optimizing CWV to improve user experience is still a recommended best practice. Monitoring real user data from the Chrome UX Report and using lab testing tools can help identify optimization opportunities to boost site speed and responsiveness.
The messaging has shifted from CWV being a distinct ranking factor to being integrated within Google's overall evaluation of user experience. But the evidence confirms page speed and stability play a role in rankings.
HTTPS
The implementation of HTTPS encryption has been confirmed by Google to provide a ranking boost, albeit minor, in search results. This preference for secure sites aims to enhance the safety of users' web experiences. But how exactly does HTTPS factor into Google's ranking algorithms?
HTTPS secures websites through SSL/TLS certificates that facilitate encrypted data transfer between servers and browsers. This protects sensitive user information entered on sites.
In 2014, Google announced they had begun using HTTPS adoption as a lightweight ranking signal. Sites served over HTTPS receive a slight ranking advantage over equivalent HTTP sites.
Importantly, this signal operates primarily as a "tiebreaker." If a secure HTTPS site and an insecure HTTP site are extremely similar in relevance and other factors, HTTPS gives the former site an edge.
However, relevance remains the dominant factor - an irrelevant HTTPS site will still lose out to a highly relevant HTTP site. The HTTPS boost only comes into play when competing pages are roughly equal otherwise.
While characterized as lightweight, industry experts recommend all sites migrate to HTTPS regardless. Even marginal ranking gains and enhanced user trust/safety are worthwhile, and Chrome now flags HTTP sites as "not secure."
Beyond the direct HTTPS signal, Google also factors server security into the page experience update rolled out in 2021. This evaluates elements like HTTPS, lack of warnings, and intrusive interstitials.
So while HTTPS alone provides a minor direct ranking increase, its security benefits also feed into page experience calculations. In a holistic sense, HTTPS offers multiple avenues to slightly strengthen search visibility and clicks.
However, HTTP sites still comprising roughly 30% of the web continue to rank well when offering high relevance. The benefits of HTTPS are not so dramatic that other signals can be ignored. HTTPS is not a silver bullet or cure-all for mediocre content.
In summary, every website should adopt HTTPS as a best practice for user privacy and security. The slight SEO perks are secondary. But for sites looking for every possible marginal ranking gain, the SEO influence of HTTPS is one more reason to migrate from HTTP.
6. User Experience (RankBrain)
User experience has become a major ranking factor with Google's increased focus on satisfaction and relevance. Signals like click-through rates, bounce rates, and engagement metrics provide insight into how well pages meet searcher needs.
Google leverages its RankBrain AI system to analyze these interactions at scale to determine the true usefulness of pages.
Specifically, Google evaluates metrics like:
- Click-through rates - The percentage of searchers who click on a listing after seeing it. Higher CTRs indicate strong relevance.
- Bounce rates - How quickly visitors leave a page. High bounce rates suggest low quality or irrelevant content.
- Time on page - The duration visitors spend engaging with content. More time signals they found it useful.
- Pogo sticking - When users quickly click back and forth between results, unsatisfied with content.
- Scroll depth - How far down a page visitors scroll before leaving. More scrolling shows engaged reading.
- On-site interactions - Clicks, downloads, signups, purchases. Conversions demonstrate highly valued content.
Essentially, Google wants pages that successfully inform, satisfy, or convert visitors according to their query and intent. Pages that quickly lose visitor attention do the opposite.
By optimizing content for engagement and relevance, you can improve user experience signals. This tells RankBrain your pages better serve needs, meriting higher rankings.
Conversely, thin content created just for keywords will suffer from lack of engagement. No amount of optimization can rescue poor content. Only truly satisfying searchers earns strong RankBrain scores.
So while you optimize for Google, never lose sight of optimizing for users first and foremost. Building authority with both users and algorithms is how you ascend in the SERPs.
Click Depth
Click depth refers to the number of clicks required to navigate from a site's homepage to any given page. In essence, it measures how deep pages are buried within a website's architecture.
Some speculate that pages with lower click depth values tend to rank better in Google search results compared to pages buried deeper from the homepage. But is click depth definitively confirmed as a Google ranking factor?
The idea is that pages farther away from the homepage tend to be more difficult for users and search engine bots to find and access. Thus, they may suffer penalties in visibility and search performance.
In a Google Webmaster Hangout, John Mueller gave a cautious indication that click depth plays a minor role. He noted if the homepage has high authority, Google may give slightly more weight to pages just 1 click away versus pages multiple clicks away.
This aligns with how crawler bots operate. Pages beyond 3 clicks from the homepage risk not being indexed at all unless a site has exceptional authority. So click depth could influence discoverability.
Additionally, click depth relates to internal PageRank flows. Homepages tend to have the highest PageRank, passing equity to pages they directly link to, which progressively diminishes with each click further away.
However, Mueller stressed click depth is an extremely minor factor in isolation. The overall quality and authority of a page matters far more than click depth alone.
In most cases, an authoritative, well-optimized page providing strong value to users can still rank well even with high click depth. The slight crawl accessibility challenges imposed by depth do not typically overrule other positive ranking signals.
So in summary, while click depth may play a subtle role in discoverability and equity passed from homepages, it is not likely strong enough to directly determine rankings. Page relevance, authority and overall quality outweigh click depth substantially.
For user experience, keeping important pages within a reasonable click depth is wise. But obsessive click depth optimization solely for rankings is largely unnecessary for most sites. Focusing on creating high-quality, authoritative pages that serve user intent is a much more productive use of SEO efforts.
7. Backlinks
Links remain one of the most influential signals for determining search rankings according to Google. There are three key types of links that matter for SEO:
Inbound Links:
Also known as backlinks, these are links from external sites pointing back to pages on your domain. High-quality backlinks from authority sites indicate trust, relevance and influence. The more backlinks you have, especially from reputable sources, the more authority is passed onto your own site.
Google evaluates backlinks based on:
- The DR (domain rating) of the referring site - Links from high DR sites carry more weight.
- Anchor text used - Descriptive, keyword-relevant anchor text is ideal. Avoid over-optimization.
- Link location on the page - Links higher on content rather than in footers/sidebars are better.
- Contextual relevance - Links embedded naturally in content on related topics are ideal.
- Link velocity - Natural link building over time is preferred vs rapid spikes.
- Link diversity - Backlinks from a variety of quality sources is better than just a few domains.
Earning backlinks should be a priority but requires a natural, ethical approach centered on creating highly shareable content. A key step in this is to analyze your competitors backlinks, using one of our tested best backlink checkers.
Outbound Links:
Outbound links from your pages to external authority sites also play a role in SEO. Linking out to quality resources demonstrates an awareness of influencers in your space. However, balance is key - avoid excessive outbound links and focus on referencing the best, most reputable sources.
8. Real Business Information
For businesses trying to rank in local search results, ensuring your real business information is up to date and consistent across the web is hugely important.
Google and other search engines want to surface reliable, accurate local business data so searchers can trust the results. Key elements include:
- NAP consistency - Having your business Name, Address and Phone number correctly displayed and matched across directories optimizes local rankings. Inconsistencies can negatively impact visibility.
- Complete Google My Business profile - Fully populating your GMB listing with images, business info, menus, hours etc. helps you stand out in local pack results.
- Positive local reviews - Earning reviews on GMB, Facebook, Yelp and other platforms builds trust and social proof. Aim for at least 20-30 reviews.
- Local citations - Being listed on directories like Yelp along with industry-specific sites signals your business is established locally.
- Optimized on-site location pages - Having a contact us page with Schema markup for your address, phone number and business hours enables rich results.
- Locally-optimized content - Incorporate local area names, keywords and links to location pages to boost local SEO.
Satisfying these factors helps search engines reliably understand your business and connect you with nearby searchers. Inconsistent or missing information creates ambiguity that can hinder your rankings.
By ensuring complete profiles, consistent NAPs, strong local signals like reviews/citations and optimized location-based content, local businesses can occupy the coveted map pack.
Appearing prominently for local searches helps drive foot traffic, calls and directions to your physical location. For any business with a brick and mortar presence, optimizing real business signals should be a local SEO priority.
9. Site Structure
A website's information architecture - how content is organized and structured into a cohesive network of pages - has a significant impact on both user experience and SEO performance. Optimizing site architecture helps visitors efficiently find information while improving crawlability for search engines.
Some key elements of an SEO-friendly site architecture include:
- Simple, flat navigation menus that allow users to reach any top-level section within 1-2 clicks from the homepage. Complex nested submenus frustratingly hide content.
- Logical semantic URL structures using keywords and natural page names. This creates readable URLs that users and search bots better understand.
- Clear visual hierarchies and layouts that direct users' attention. Strong calls-to-action, effective sidebar/footer links, and distinct content sections prevent confusion.
- Consistent site-wide header, footer, sidebar, and navigation elements. Following conventions reassures visitors.
- Intuitive internal linking schemes between related content improves discoverability and cross-navigation.
- Appropriate use of tabs or pagination to segment lengthy content yet keep it interconnected.
- Effective internal site search for lookup on expansive sites.
- Tagging and categorization to facilitate browsing and filter abilities.
By making content easy to digest and navigate between, users can satisfy their intent efficiently. This increases engagement metrics that Google monitors like lower bounce rates, more time on site, and higher on-site conversions.
Well-planned architecture also allows crawlers to smoothly index the entire site, reducing issues with orphaned pages. This expanded indexation surfaces more pages in search engines.
With user experience being central to rankings today, flaws in site architecture negatively impact performance. In contrast, making pages intuitively accessible improves perception among search algorithms.
10. Internal Linking Structure
A website's internal linking structure - how pages connect to and reference each other via hyperlinks - can significantly influence both user experience and SEO performance. Strategic internal linking helps guide visitors to related content while enabling search bots to better crawl and index sites.
Some best practices for structuring internal links include:
- Linking to related content from within paragraph text rather than just menus/footers. These contextual links boost discoverability.
- Using keywords and phrases as anchor text rather than over-optimized exact matches. Variety feels more natural.
- Linking deeper pages to high authority pages like the home, about us, and category/section pages to pass equity.
- Implementing canonical tags on duplicate content pages to signal the original. Prevents diluted equity.
- Creating hub or pillar pages with lots of internal links to provide link juice to surrounding pages.
- Interspersing internal links throughout content rather than just listing links at the end.
- Having clear calls-to-action linking to landing pages, product pages, contact pages, etc to facilitate conversions.
- Structuring related content in linked clusters around topics. This builds relevancy.
- Using descriptive labels for links to inform users like "Learn more about our services."
Proper internal link structures make it easy for users to navigate sites by providing pathways between relevant pages. This can increase time on site, lower bounce rates, and enable conversions through improved user journeys.
For SEO, interlinking pages also demonstrates relationships and passes authority from older, more established pages to newer ones. It also expands indexation by surfacing pages that might otherwise get orphaned.
With user experience becoming a central ranking factor, smart internal linking satisfies both visitors and search algorithms simultaneously. It turns linking into a user acquisition strategy beyond just an SEO tactic.
What Is E-E-A-T and Is It A Ranking Factor?
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness - core qualities Google's algorithms aim to identify in content as part of determining search rankings. But there is debate around whether E-E-A-T should be considered a concrete ranking factor itself.
E-E-A-T originated as a guideline for Google's search quality raters to evaluate algorithm changes and sample search results. It provides important benchmarks for assessing the expertise and trustworthiness of pages.
Given its prominence in rating guidelines, many presume E-E-A-T must directly influence rankings as a factor. But Google has clarified this is not the case.
Rather than a singular ranking factor, E-E-A-T represents a philosophical approach Google has baked into its algorithms. The search algorithms incorporate many signals that help surface pages expressing strong E-E-A-T qualities.
So E-E-A-T serves as more of an umbrella concept encompassing multitudes of granular ranking signals - things like author expertise markers, citation patterns, content accuracy, community reputation, real-world credentials, adherence to quality standards, and more.
But Google avoids referring to E-E-A-T independently as a ranking factor. As they advise:
"Our automated systems use a mix of many different signals to rank great content. We’ve tried to make this mix align with what human beings would agree is great content as they would assess it according to E-E-A-T criteria."
This distinction is nuanced but important. Google wants sites to think about aligning content with E-E-A-T ideals rather than mechanically trying to reverse-engineer it as a singular algorithmic factor.
Producing high-quality, authoritative content that earns user trust should be the goal. Google's algorithms will recognize such content based on the complete mix of ranking signals they analyze that correspond with E-E-A-T qualities.
So in summary, while E-E-A-T is not an official ranking factor, optimizing for it improves search performance by better satisfying the combination of ranking signals Google utilizes related to expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness.
Yandex Leak of Ranking Factors
In January 2023, an extensive trove of data was leaked related to the search engine Yandex, including spreadsheets purportedly listing over 1,900 ranking factors and machine learning models they use. This provides a rare glimpse into the inner workings of a major search engine.
While Yandex and Google have differences, there are intriguing parallels in terms of ranking philosophies and algorithmic approaches. The leak hints at the enormous complexity behind modern search engines.
Some key insights include:
- The number of granular ranking signals analyzed likely totals in the thousands, despite assumptions only a few hundred exist. This aligns with Google's indications they've moved beyond simplifying their algorithm to 200+ factors.
- Ranking factors are heavily customized for different query intents and content via advanced machine learning. One model called MatrixNet specializes in classifying searches and applying tailored ranking formulas.
- Some factors mirror established SEO wisdom like minimizing crawl depth for key pages and varying anchor text patterns naturally. This lends credence to those optimization techniques.
- Ranking factors are meticulously organized in spreadsheets for engineering purposes, questioning notions no one fully grasps Google's algorithm. Maintaining rank factors likely requires documentation.
- No evidence yet connects expert authorship signals like author bios to the rankings, despite a Yandex update targeting expertise and authoritativeness. More analysis is required.
The trove of data will take time to fully explore and decipher in terms of connecting factors to observable search behavior. Independent experts advise avoiding direct extrapolation of Yandex factors to Google.
But the leak provides invaluable perspective on ranking complexities, machine learning applications, and broad algorithmic approaches employed at scale by a major search competitor. These insights can lead to more informed SEO strategies through better understanding the "why" behind search engines.
While not providing clear SEO instructions, the transparency afforded by such leaks advances the industry's comprehension of search algorithms and how to craft content optimized for relevance and quality - the true purpose of SEO.
Quick Reference List of SEO Factors & Tools
On-Page SEO Ranking Factors
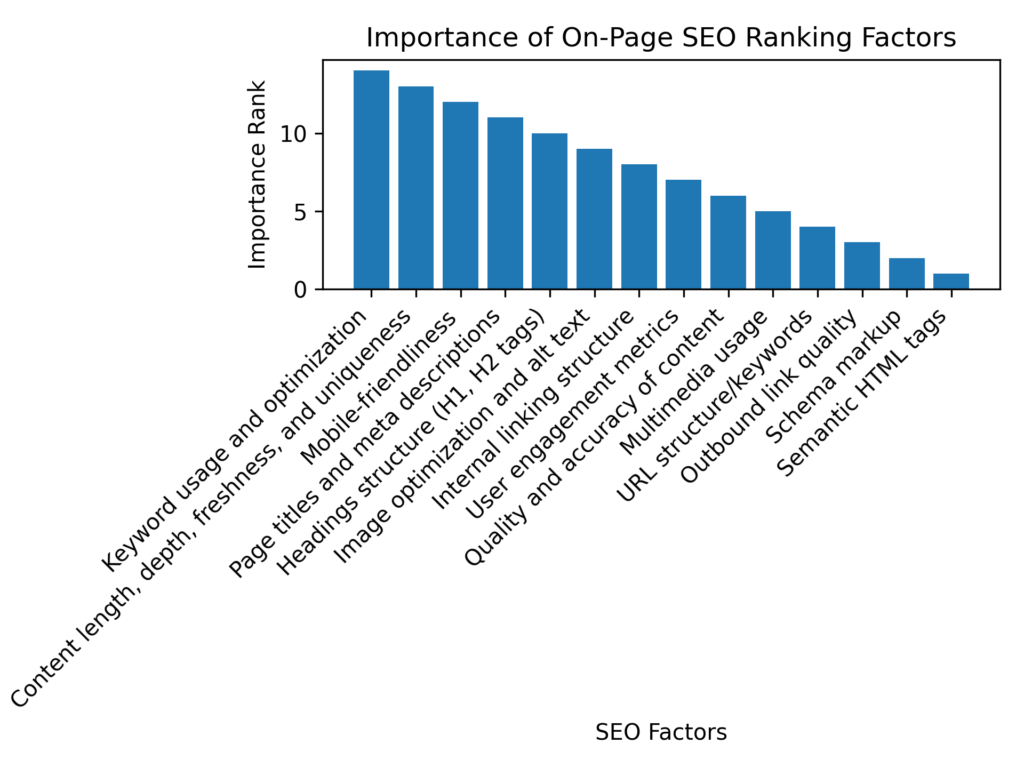
- Keyword usage and optimization - Organically incorporate target keywords in headings, content, URLs, alt text, etc. without over-optimizing.
- Page titles and meta descriptions - Craft compelling, keyword-rich titles under 60 chars and meta descriptions 150-160 chars long.
- Headings structure (H1, H2 tags) - Properly structure headings using H1 for the title, H2 for main sections, H3 for subsections to establish hierarchy.
- Image optimization and alt text - Add descriptive, keyword-focused alt text to all images to improve image SEO.
- Content length, depth, freshness, and uniqueness - Create long-form, in-depth content that provides value readers can't find elsewhere.
- Mobile-friendliness - Use a responsive design and check that content displays and functions easily on mobile devices.
- Multimedia usage - Incorporate relevant videos, gifs, and interactive elements to boost engagement.
- Internal linking structure - Link to related content, pillars, and landing pages using keywords to build an intuitive site architecture.
- URL structure/keywords - Use search-friendly URLs with dashes that include primary keywords and page names.
- Outbound link quality - Link out to credible external sources to demonstrate expertise and enrich content.
- Schema markup - Add appropriate schema like FAQ, local business, products, etc. to generate rich snippets.
- User engagement metrics - Monitor and optimize to reduce bounce rate and increase pages per session, conversions, etc.
- Semantic HTML tags - Use tags like , , etc. to structure and identify content elements.
- Quality and accuracy of content - Create content that provides true value, accuracy, depth, and uniqueness to earn trust and links.
On-Page SEO Tools
Read our list of the top on-page SEO Tools.
Off-Page SEO Ranking Factors
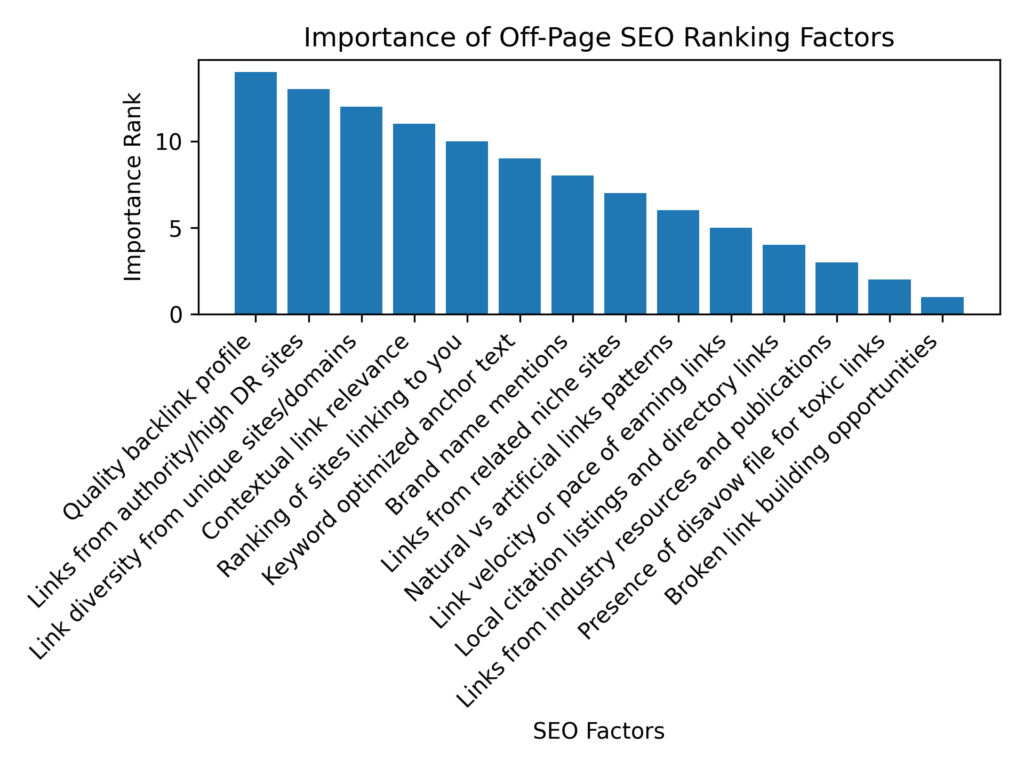
- Quality backlink profile - Build links from authoritative sites through outreach, guest posts, resource pages, etc.
- Brand name mentions - Pursue press coverage, interviews, partnerships and sponsorships to increase brand visibility.
- Keyword optimized anchor text - Vary anchor text using keywords naturally but avoid overoptimization.
- Link velocity or pace of earning links - Build links at a gradual, steady pace to avoid artificial growth patterns.
- Link diversity from unique sites/domains - Earn links from a wide variety of reputable sites rather than just a handful.
- Links from authority/high DR sites - Guest post and earn links particularly from industry leaders and authority domains.
- Contextual link relevance - Seek links from sites producing topically relevant content to convey authority.
- Ranking of sites linking to you - Aim to get links from sites ranking well themselves for industry keywords.
- Local citation listings and directory links - List your business on every relevant local directory and review site.
- Presence of disavow file for toxic links - Disavow low quality links using Google's link disavowal tool.
- Links from related niche sites - Guest post and connect with blogs and resources targeting your niche.
- Natural vs artificial links patterns - Build links slowly over time through outreach and relationships to appear natural.
- Links from industry resources and publications - Become a contributor to leading publications to build authoritative links.
- Broken link building opportunities - Find and report broken links to replace them with links back to your content.
Off-Page SEO Tools
Technical SEO Ranking Factors
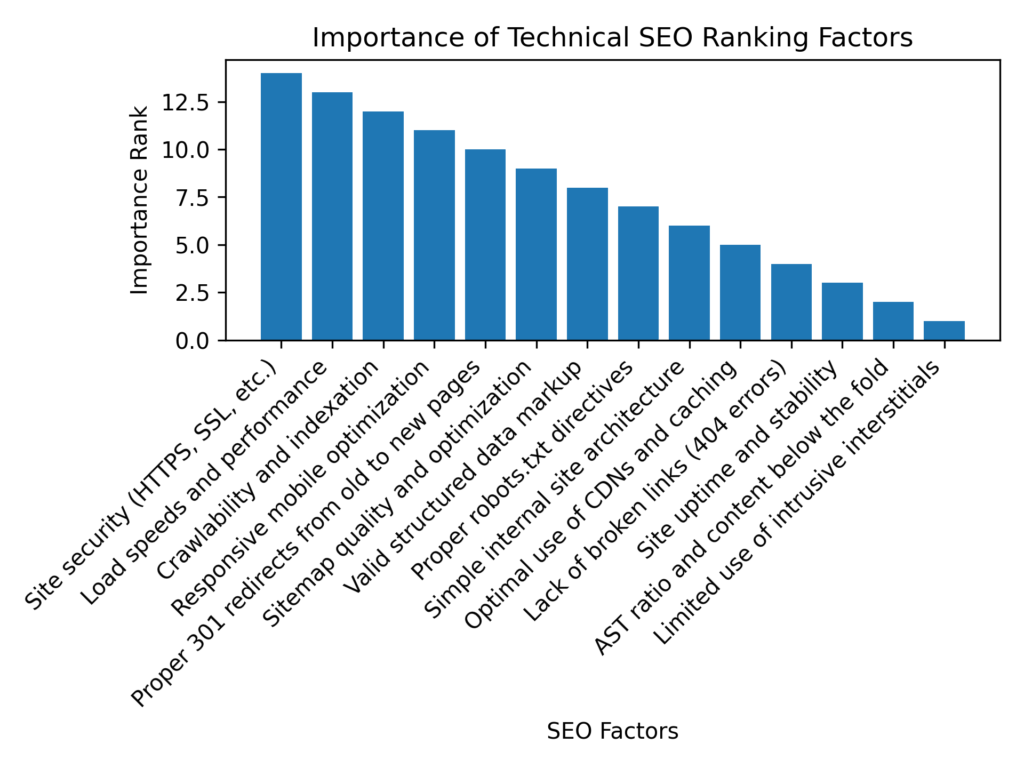
- Site security (HTTPS, SSL, etc.) - Migrate your site to HTTPS using an SSL certificate to encrypt traffic.
- Proper robots.txt directives - Configure your robots.txt file to control how search bots access non-public pages.
- Valid structured data markup - Add schema markup to enable rich results, snippets, and rankings boosts.
- Sitemap quality and optimization - Create and submit XML sitemaps to improve indexing of new pages.
- Crawlability and indexation - Fix technical issues preventing pages from being crawled and indexed.
- Load speeds and performance - Optimize images, enable caching, minify code and more to improve page speeds.
- Responsive mobile optimization - Use a mobile-friendly design and test to ensure full functionality on mobile devices.
- Proper 301 redirects from old to new pages - Redirect outdated URLs to relevant active URLs using proper 301 redirects.
- Simple internal site architecture - Design easy-to-navigate site structures with important pages prominently linked.
- Optimal use of CDNs and caching - Implement content delivery networks andcaching best practices.
- Lack of broken links (404 errors) - Identify and fix broken links to avoid negative user experience signals.
- AST ratio and content below the fold - Maintain reasonable ad-to-content ratios and enough visible above-the-fold content..
- Site uptime and stability - Monitor and address downtime issues to ensure continuous site availability.
- Limited use of intrusive interstitials - Avoid excessive pop-ups and overlays that disrupt user experience.
Technical SEO Tools
- ScreamingFrog Review
- Sitebulb
- Lumar
Read our guide on the top technical SEO Tools
Local SEO Ranking Factors
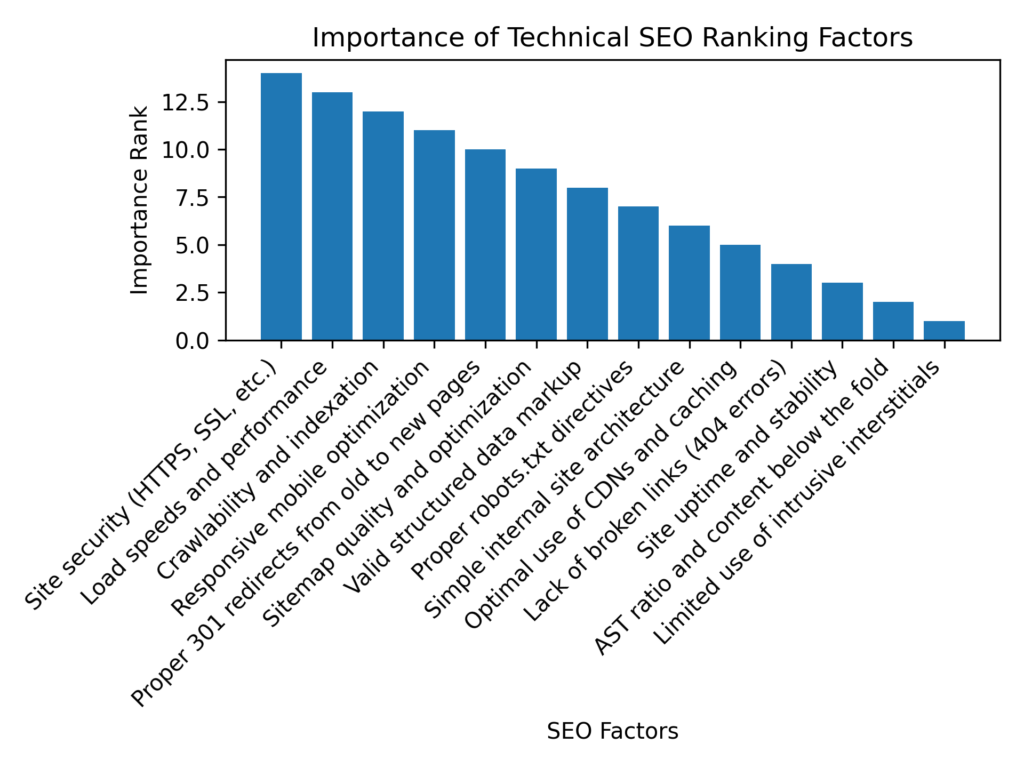
- NAP consistency - Ensure business name, address and phone number are consistently listed across directories, citations and sites.
- GMB profile optimization - Fully complete Google My Business profile with images, description, hours, services, etc.
- Positive local reviews and ratings - Build reviews on Google, Facebook, Yelp and other platforms to establish trust.
- Location pages and contact info - Create dedicated location pages with accurate business info and schema markup.
- Local keywords and area names - Target keywords incorporating your city, county, neighborhood, etc.
- On-site business schema markup - Implement local business schema highlighting key details like address and opening hours.
- Citations like Yelp, Foursquare, etc. - List your business on every relevant local citation site possible.
- Link signals from locality sites - Pursue links from neighborhood blogs, city guides, local publications, etc.
- Membership of relevant directories - Get listed in top local/niche directories related to your business category.
- Optimization for "near me" searches - Create content targeting searches for your products/services + "near me."
- Local landing pages and conversion paths - Design localized site flows guiding visitors to conversions.
- Image SEO with location visuals - Use local imagery and ensure it is geotagged.
- Optimization of Google Posts - Leverage Google Posts to highlight events, offers, and updates.
- Ranking for category/product + location - Target keywords using your service/product terms plus geographic location.
- Embedding GMB maps onto website Footer- Ensure you embed your Google Business Profile into the footer of your site.
Local SEO Tools
FAQ
How often does Google update its ranking algorithms?
Google makes hundreds of changes and updates to its algorithms every year. Major identifiable updates occur less frequently
Directly no, but social signals can indirectly boost rankings by increasing visibility, clicks, and brand awareness.
Does keyword density matter for SEO?
Not as much anymore. Focus is on organic use, quality content, and satisfying intent rather than exact keyword density.
Can poor website security or too many ads hurt rankings?
Yes, site security vulnerabilities and disruptive ads negatively impact user experience, which Google may penalize.
How long do new pages and content take to start ranking?
It varies, but typically 1-3 months for new pages to begin indexing and ranking provided they are optimized.


