On-page SEO, off-page SEO, and technical SEO. These are the three interconnected pillars that impact your website's search engine rankings. Get them all balanced just right, and you'll be crushing it on your way to the top of the SERPs.
Easy to say, tougher to do. And that’s precisely why the field of search engine optimization exists: To tease apart and build upon the individual ranking factors and techniques that Google's algorithm uses in prioritizing websites in search results.
Google is very transparent about the fact that its primary goal is to provide users with relevant search results that match their search intent. So, fundamentally, SEO is all about proving to the Google algorithm that your website is well-organized, authoritative, unique, and engaging.
But how do you go about doing that?
In large part, with consistent attention to on-page SEO strategies.
In this ultimate guide, I'll show you how on-page SEO can be a game-changer for your website's rankings and also how you can make it a manageable part of your daily routine. I'll provide an in-depth overview of on-page SEO basics along with practical tips on how to implement them for your own website. At the end, I'll also provide an incredible free tool to help you get started (my personal on-page checklist).
What are we waiting for? Let's get started!
What Is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to the optimization of your website's internal components. Its goal? To increase organic traffic flow and search engine rankings.
Both front-end and back-end elements are included in on-page SEO. As we'll see later in this guide, it can even overlap with technical SEO to a large extent (though not off-page SEO, which focuses on external signals beyond the parameters of your website).
Unlike off-page SEO, on-page SEO is entirely within your control as a website owner. So, if you don't stay on top of it you've only got yourself to blame. Personally, I find this motivating rather than intimidating. I prefer it when the reins are in my own hands!
Here's an overview of what's included in on-page SEO (not an exhaustive list):
- Title tag optimization
- Meta description optimization
- Heading and subheading optimization
- Content optimization
- Image optimization
- Internal linking
- URL structure
- Technical SEO (to an extent)
- Mobile optimization
I'll cover all of these areas in more depth below, plus much more.
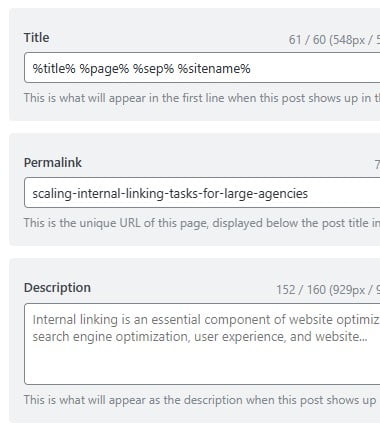
Title Tag Optimization

Title tags are portions of HTML code that signal the title of a given webpage. In HTML, a title tag is located in the <head> section of code and is indicated by <title> at its beginning and end. For example, <title>How To Do On-Page SEO<title>.
Title tags help Google understand what a given webpage is about. They show up in search results, social media, and browser tabs and are an important (and confirmed) Google ranking factor. Title tags can effectively increase organic traffic when properly optimized.
Best Practices for Writing Effective Title Tags
- Use relevant and targeted keywords - Select title tag keywords strategically to ensure that they provide a clear snapshot of what your webpage is about. Many SEO professionals consider title tags to be one of the most potent ranking factors, so use them as an opportunity to foreground important keywords.
- Keep title tags concise and to the point - Short and sweet—but still smart and strategic—is best when it comes to title tags. Google and Google users will both appreciate a title tag that provides all the info they need about a webpage without running on and on. 50-60 characters is an optimal length to aim for.
- Use modifiers to stand out in search results - Modifiers are words that Google users might add to a general search to make it more specific. Common examples include best, simple, course, reviews, easy, and dates (such as the year). Title tag modifiers can help pages to rank for long-tail keywords. For example, On-Page SEO 2023 or Best On-Page SEO Guide. You might also consider including your brand name in title tags.
Tips for Optimizing Title Tags on Different Types of Pages
Homepage Title Tags
The title tag for your homepage will likely be your most branded title tag. It should include the name of your business and clearly demonstrate its purpose.
Category & Subcategory Page Title Tags
Category and subcategory title tags can easily become repetitive—but don't let them! Make absolutely certain that each and every category and subcategory title tag is unique.
Product Page Title Tags
Consider including one or more of the following in product page title tags: Product title, brand, category, and CTA. Avoid automated title tag generation where possible.
Blog Post Title Tags
Highlight your content while also including a keyword, if possible. If your title is catchy or provokes an emotional response, so much the better.
Service Page Title Tags
Make each service page title tag clear and unique. Short and simple is best.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Writing Title Tags
- Keyword Stuffing - Keyword stuffing is the practice of attempting to unnaturally fit too many keywords (or the same keyword too many times) into tags or content. Don't just avoid this practice for title tags; avoid it everywhere on your website or risk penalties.
- Duplicate Title Tags - When you give two pages identical title tags, you're wasting an opportunity to optimize them each separately. Not only that, but duplicate page content can also lower your ranking status.
- Using overly long title tags - Aside from being impractical, long title tags can actually get cut off and/or modified by Google. Neither of these scenarios will boost your SEO or impress potential visitors.
Using Title Tag Tools & Resources
Google Search Console
Google Search Console offers powerful keyword research capabilities that can help you identify the words you should be targeting in your title tags.
Semrush
Semrush's Site Audit tool can help alert you to missing and/or duplicate title tags within your website.
Ahrefs
The Ahrefs SEO Analyzer Tool allows you to easily keep tabs on all of the title tags on your website.
Meta Description Optimization
You know those little descriptions beneath title tags on search engine results pages? Those are meta descriptions. Meta descriptions are HTML tags that summarize the purpose of a given page or post and typically should not exceed about 155 characters.
While meta descriptions aren't used in ranking algorithms and therefore don't directly impact SEO, they do still play an important role in attracting visitors to your site. A compelling meta description can make all the difference between someone choosing to click through to your page or skimming past it to the result above or below.
The Importance of Compelling Meta Descriptions
As the old saying goes, you can lead a horse to water, but you can't make him drink. In the SEO industry, we could just as easily say you can improve a site's rankings, but you can't make people click.
In other words, ranking factors can only take you so far. Ultimately, to improve click-through rates (the percentage of people who actually click on your site), you need to demonstrate to Google users why your site is the best, most relevant site to answer their query. And you need to do it quickly—sometimes so quickly that they're not even conscious of the process.
And this is where compelling meta descriptions come into play. A well-written meta description can literally be the deciding factor that determines whether someone selects your site from the SERPs or passes it by.
As with every element of your website, you want to ensure that your meta descriptions are providing a superior and impactful user experience.
Tips for Writing Effective Meta Descriptions
- Use relevant and targeted keywords - Just as with title tags, you want to select a keyword (or keywords) to use in meta descriptions that will match Google users' search intent.
- Keep meta descriptions concise and to the point - Remember, you've got 155 characters to make your pitch, so focus on your core message and don't waste space with extraneous words or information.
- Use a call-to-action to encourage clicks - Read this! Download our free guide here! These are examples of the types of calls to action that can motivate users to click on your page.
- Use formatting and punctuation to stand out - Search engine results pages are busy places filled with competing options and messages. Consider using a question, exclamation, quote, or bolded lettering to make your meta description pop out from the crowd.
Optimizing Meta Descriptions for Different Types of Pages
Homepage Meta Descriptions
For your homepage, simply offer a clear overview of what your site is about and, ideally, a compelling reason to click on the title tag.
Category & Subcategory Page Meta Descriptions
Category or subcategory page meta descriptions should communicate what defines the products on that particular page. You can also include a simple action phrase, such as, shop for women's running shoes.
Product Page Meta Descriptions
When it comes to product page meta descriptions, it's all about showing potential customers the benefit they'll get from your particular product. Take them on a (very short) mind journey, such as never worrying about scratchy sheets again.
Blog Post Meta Descriptions
When people are searching for information, they want to know why it will be worth their time to read an entire blog post. A good blog post meta description will demonstrate exactly that and perhaps also establish an emotional connection. For example, Tired of your pie crust always burning? Learn 5 easy tricks for guaranteeing perfect pies every time.
Service Page Meta Descriptions
A good service page meta description will describe the service offered as well as why it's superior to other similar services. For instance, The fastest oil change in town will have you back to your day in no time.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Writing Meta Descriptions
- Keyword stuffing - Keyword stuffing is a practice to be avoided in all on-page optimization, including in meta descriptions.
- Duplicate meta descriptions - Likewise, duplicate content is a wasted opportunity and has the potential to lower your rankings no matter where or how it's used on your site.
- Overly long meta descriptions - As with title tags, Google will re-write or cut off overly long meta descriptions, which is not ideal. Try to stay under about 155 characters.
- Not including a call-to-action - Meta descriptions that lack a call-to-action have missed an opportunity to compel a potential customer to click.
Heading & Subheading Optimization
Headings and subheadings are the in-text titles that break content into organized and manageable sections. They help users and search engines alike skim content and understand what it's about without having to read every single word.
The role of headings and subheadings in SEO is to help Google understand the structure of a given page. H1 headings are typically the broadest headings (titles, for instance), while H2, H3, and H4 headings break content down into smaller, more detailed categories. Once Google understands a page's hierarchy, it can better ascertain how relevant that page will be to a user's search intent.
The Importance of Clear & Effective Headings & Subheadings
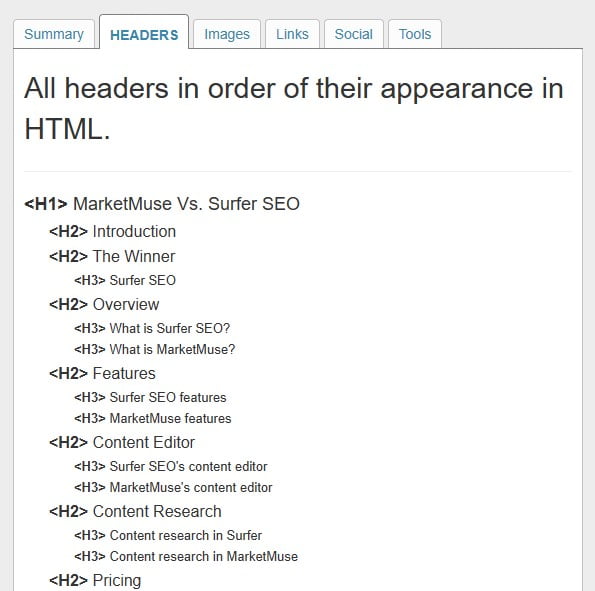
No one likes to stare at a wall of solid text, and when visitors encounter one they tend to turn tail really quickly. Headings break up content into digestible bites and allow people to get directly to the heart of the information they're seeking without having to waste time reading a zillion paragraphs. I think this graphic from Semrush sums it up perfectly.
So, yes, headings are super instrumental for positive user experience, but they're also equally important for search engines. When Google understands the structure of your page and what it's all about, it will rank your page higher for relevant keyword searches.
Tips for Creating Compelling Headings & Subheadings
- Use relevant and targeted keywords - This one again. As you can see, being savvy about where you include keywords and phrases is vital to on-page SEO success.
- Use modifiers to stand out - If you have a lot of headings and subheadings, don't get overzealous with modifiers (it can start to sound tacky). But do use them strategically within your hierarchy of headings to capture those long-tail keywords.
- Use formatting to your advantage - Play around with eye-catching fonts, spacing, colors, and other text formatting options to keep users scrolling down your page.
Tips for Organizing Content Using Headings & Subheadings
- Create a clear hierarchy of headings and subheadings - Using headings to break up content is only effective if the headings follow a logical structure and are clearly organized. All subheadings should fall under the umbrella of your H1 heading and should move from broader to more detailed information as they progress (H2, H3, H4, etc.).
- Use subheadings to break up content - Headings divide content into manageable chunks that help users not to feel overwhelmed. When implemented thoughtfully, they can greatly improve the readability of your content.
- Balance headings with other formatting elements - There's no doubt that headings and subheadings are a crucial element of readability, but don't make the mistake of relying on them in isolation. Other effective formatting elements that can also make your content more inviting include bulleted points, short paragraphs, images, and more.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Using Headings & Subheadings
- Keyword Stuffing - Once again, a definite no-no.
- Overly long headings - Headings and subheadings should be quickly digestible. Save the long stuff for your paragraphs.
- Not creating a clear hierarchy for headings - As I already mentioned, this is a big one. Keeping your headings and subheadings organized and logically connected is critical for search engines and human readers alike.
- Overusing headings - It's probably more common to underuse headings and subheadings than to overuse them, but both should be avoided to keep readability flowing.
Content Optimization
Content optimization is the process of creating content that search engines can understand, evaluate, and disseminate to the largest relevant audience possible. You could have the most outstanding content in the world, but without optimization it might remain buried on the 25th page, never to be seen by your target audience of Google users.
So, how do you effectively optimize content? I've already covered some of the major strategies above, but let's take a look at some more:
Key Factors for Content Optimization
- Word count - There's no magic optimal length for content, but steer clear of content that's too short. Assuming it's relevant and high-quality, longer content provides more opportunities to rank for keywords and gives search engines a more in-depth understanding of what your page is about. To determine a word count estimate for any given piece of content, consider your keyword research, the past performance of similar content on your site, and the length of any content you may be directly competing with.
- Keyword density - Keyword density refers to the number of times a given keyword appears in a piece of content. While repeating important keywords a few times in a piece of content is recommended, keyword stuffing is definitely to be avoided.
- NLP keyword/entities - Including NLP keywords and entities in content has become a key aspect of optimization. There are many different tools that can help you extract and compile relevant NLP keywords from competitor content.
- Answers questions from "People Also Ask" - Google's People Also Ask rich snippet is an excellent source of potential information to include in your content optimization strategy.
- Headings and images - I've already covered the importance of these elements in breaking up content and making it digestible for search engines and human users alike.
- Unique content - This one is huge. Like blue whale huge. Content that's got something fresh and relevant (and well-optimized) to offer will blow the competition out of the water.
- Bolded words - Bolded words can help search engines understand important components of your content and rank your page accordingly.
- Internal linking - This is definitely a content optimization strategy not to overlook. I'll cover it in more detail below.
Avoiding Over-Optimization of Content
In all things there must be a balance—including content optimization. If you optimize your content to the point where it feels unnatural (known as over-optimization), it can put search engine bots on alert and actually jeopardize your organic traffic flow.
Examples of over-optimization can include ranking for non-relevant keywords, using multiple H1 headings on pages, or pointing too many links to specific pages.
Here's my best advice for avoiding content over-optimization: Don't try too hard! Create original, high-quality content that speaks for itself and optimize it using tried and true principles. The results of keeping it real will not disappoint.
Also, it doesn't hurt to have an outstanding content optimization tool at your fingertips to do the bulk of the heavy lifting for you. Surfer and On-Page.AI are a couple of my personal favorites.
Using Surfer SEO for Content Optimization
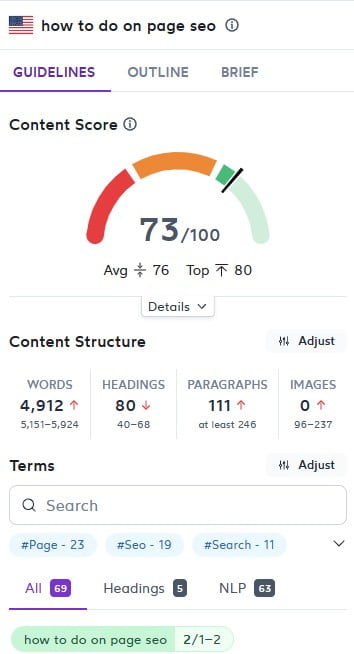
Surfer SEO is a behemoth of an on-page optimization tool, and it's especially fine-tuned for written content optimization. Essentially, it analyzes your page content against more than 500 SEO signals and helps you compete directly against your top competitors.
Surfer's main features include its next-level content editor as well as its keyword research tool, audit tool, and growth management tool (Grow Flow). I highly recommend Surfer as a content optimization tool in general, but especially if you're looking to dramatically improve the quality of your written content.
Using On-Page.ai for Content Optimization
On-Page.ai is a newer content optimization tool that uses artificial intelligence to help you outrank your competition. The platform offers a new and interesting approach to content optimization that sets it apart from other popular tools. I believe that used effectively, On-Page.ai has the potential to put your content (and whole website) ahead of the SEO curve.
On-Page.ai's core features include its website crawler, content creation software, tracking software, keyword tool, and highly related terms tool (which I'm a big fan of).
I do have one caveat regarding On-Page.ai, and that is that it's a platform best suited for SEO professionals (or at least those with quite a bit of optimization experience). If you're just starting out, I'd recommend Surfer SEO instead.
Call-To-Action Buttons
Get started with Surfer SEO's free 7-day trial!
Try out On-Page.ai for yourself here!
Image Optimization
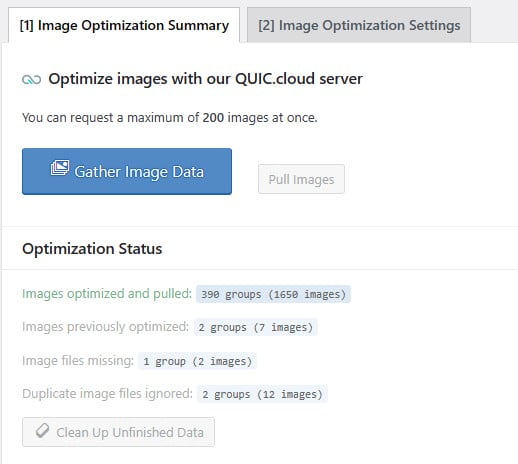
Like other optimization techniques, image optimization is all about improving rankings. It can help your website's images rank in Google Images and can also help improve your website's rankings overall.
One critical element of image optimization is to maintain high image quality while also reducing file size as much as possible to decrease page load times. Another is to maximize the SEO potential within image alt text and image file names.
I’ll break these elements down a little further:
Optimizing Image File Size
Website performance has a significant influence on SEO, and the last thing you want are large, unoptimized images slowing down your page load times. Smaller images load more quickly than large ones, but before you go indiscriminately reducing all your images, remember that image quality decreases along with file size. And you definitely want to avoid having poor quality images on your website (no one’s a fan of that).
So, how do you nail the perfect SEO balance between image size and quality? While there are many platforms and templates that can automate image sizing for you, here are a few fundamentals to keep in mind:
- Use reputable image software to reduce the size of large images.
- Select the correct image format for your purpose. JPEG files may be your default, but consider the benefit of small PNGs for simple decorative elements and avoid GIFs for large images.
- Thumbnail images should always be as small as possible (quality is not so much of a factor in this context).
- Carefully consider the aesthetic benefit of decorative images vs. the amount they may slow down your load times. Optimize accordingly.
Optimizing Image File Names & Alt Text
Did you know that 10.1% of all Google searches are for images? Or, in other words, that about 1 billion people use Google images every single day? Obviously, you want your website to get a piece of that pie, which means you've got to optimize your image alt text and file names accordingly.
Alt text (alternative text) is HTML text that describes an image on your website. It simultaneouslyprovides context to search engine crawlers and allows images to be explained out loud (mainly for users with visual impairment). When writing alt text, here a few best practices:
- Include a target keyword, if possible.
- Keep it under 125 characters.
- Avoid phrases like picture of or image of, as these aren’t necessary.
- Don't add alt text to decorative graphics or images.
Image file names may seem insignificant, but remember that they, too, help Google learn about your page content. Avoid generic or numerical image file names in favor of simple but clear descriptions. For example, dog-eating-bone.jpg or rainbow-umbrella.jpg.
Adding Geo-Tags for Local Businesses
One of the defining features of SEO for local businesses (Local SEO) is the fact that the target audience is located within specific geographical parameters. Geotagging is the practice of adding geographical data to images (or other media) and can be a massive benefit for putting your business on the map—literally (the Google Map, that is).
Optimizing and geotagging images is considered best practice for enhancing your GMB listing and organic traffic. It can be a defining factor in whether or not potential customers easily discover and locate your business.
You can use a number of different tools (such as GeoImgr) to add geotags to images. Most smartphones and cameras can now add GPS data to images automatically, so ensure this feature is enabled if you’re planning to geotag the pictures you're taking.
Applying Width & Height Tags to Images
Applying width and height tags to images is another way to improve your website's performance and user experience (which both impact SEO). When images load after text, they can cause pages to flicker or the text to readjust. This is irritating and can be avoided by reserving the height and width of an image even before it loads. Here's how.
Tools & Plugins for Image Optimization
There are many image optimization tools on the market. Here are a few examples I'd recommend:
- Adobe Photoshop - A fully loaded image design and editing suite
- Kraken.io - A WordPress plugin for fast image optimization and resizing
- Compressor.io - This high-quality image compression tool can accommodate JPEG, PNG, SVG, GIF, and WEBP images
- Imagify - Image compression is made simple with this plugin
- ShortPixel - ShortPixel is a lightweight image optimization plugin that will automatically compress your image files
- EWWW Image Optimizer - This cloud-based tool offers automated compression and image optimization solutions
Internal Linking
Internal linking is the process of creating links between the pages on your website. But why is it important for on-page SEO?
The Benefits of Internal Linking
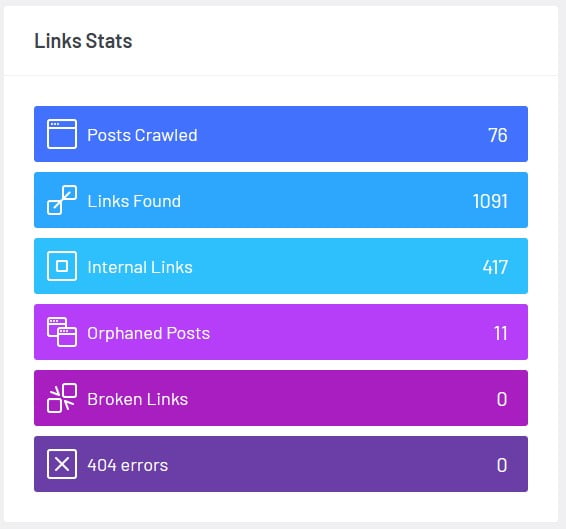
Internal linking helps search engines to find and index pages; it defines your website's overall structure; it transfers page authority from high authority pages to lower authority pages; and it helps search engines understand the context of your website.
And that's without even factoring in real, live users!
Internal linking enhances user experience by making navigation easier. It embeds opportunities for users to explore your site in logical and meaningful ways, and can organically move them further down your sales funnel. Of course, this can also result in increased dwell time, which is another SEO booster! Win-win.
Anchor Text & Internal Linking
Anchor text is the clickable text in an internal link (or any link, for that matter) that takes users to a new location. And guess what? It's important for SEO.
The anchor text for internal links helps search engines put a page in context based on the pages it's linked to. Here are some tips for optimizing your anchor text for internal links to get the most SEO value out of them:
Best Practices for Internal Linking
- Use descriptive and keyword-rich anchor text - Including keywords in anchor text may be a no-brainer, but don't make the mistake of repeating the same anchor text multiple times, not even on separate pages. Every anchor text should be compelling and unique.
- Link to relevant pages - Internal links should never be random or haphazard. Rather, they should help users and search engines alike navigate your site and connect information in meaningful ways.
- Use a hierarchical linking structure - One of the ways that Google finds pages and determines their importance is by the number of internal links pointing to them. Use this knowledge to help you communicate the intended architecture of your website. Remember, navigational links are internal links too.
- Link to deep pages, not just your homepage - Internal links are like the veins and arteries that keep traffic flowing through your website. Make sure that you're getting oxygen to all the vital parts, no matter how far from the homepage.
Strategies for Linking to Different Types of Pages
- Contextual linking - These types of links are embedded within the content to provide additional contextual information or resources to users. They're probably the most impactful for on-page SEO.
- Navigational linking - Navigational links often appear in a navigation menu but may also be strategically located elsewhere on your website.
- Footer linking - Footer links are sitewide links that appear at the bottom of every page on your website.
- Sidebar linking - Like footer links, sidebar links are sitewide and can be used to feature popular content or for navigation purposes, among other things.
Avoiding Orphaned Pages
Orphaned pages are pages on your website that don't have any internal links pointing to them. Not surprisingly, they're tough for search engine crawlers to find and index. They're also hard for human users to discover.
Creating and maintaining a clear sitemap can help you avoid orphaned pages, as can regularly auditing your site using reputable software such as Semrush or Screaming Frog (which will both alert you to any orphaned pages that may have slipped through the cracks).
Tools & Plugins for Internal Linking
Internal linking is not a process that can be fully automated (at least not yet), but the three programs below can do a lot of the legwork for you. I'd recommend using one of these three platforms to improve your internal linking (especially if you have a large website with a lot of historical posts):
- Link Whisper - This platform is fully dedicated to internal link building and is continually evolving. My personal number-one pick.
- Ahrefs - The Ahrefs site audit tool can help you review and repair your internal link structure.
- Semrush - Semrush's site audit includes an internal linking report with metrics for a whole range of internal link issues all in one place.
External Linking
External links are links on your website that point to other websites (not to be confused with backlinks, which point from another website to yours). While it may seem counterintuitive, external links are actually important for SEO. Rather than detracting from your website’s authority, they actually help to contextualize your website and build up its authority.
Of course, this is only true if the external links you include on your website are relevant, strategically placed, and link to high-quality, high-authority content.
URL Structure
URL structure is basically just what it sounds like—the way that the URLs of the pages on your website are written, as well as how they reflect and enhance its overall structure. URL structure is important for on-page SEO because it can both improve user experience and help Google better understand what each page on your website is all about.
Best Practices for URL Structure
- Keep URLs short and easy to read - Search engines and human users will both appreciate URLs that are uncluttered and straightforward. Avoid irrelevant numbers and publish dates.
- Use hyphens to separate words in URLs - This simply improves readability and communicates page purpose with clarity.
- Use a hierarchy in your URL structure - It’s important that your URL structure remains consistent as you create various posts and types of internal pages. Consider your website’s overall page hierarchy and create logical URLs accordingly. (For example, this URL makes it clear where my Semrush review fits in the hierarchy of the SerpFocus website https://serpfocus.com/review/semrush/).
The Role of Keywords in URL Structure
I’m sure it won’t come as a surprise that using keywords in URLs can have SEO benefits. But you’ve got to be strategic about how you do it. As with keyword optimization for any on-page element, URL keywords must be targeted and relevant. Consider the topic of your content as well as the main keywords you’re trying to rank for and select a keyword to include in your URL accordingly. But don’t go overboard. Not every URL needs to include a keyword.
URL Structure & Crawlability
Google’s crawlers move from page to page on your website discovering new content, indexing it, and filling in Google’s understanding of your site’s purpose, context, authority, and more. How do they do all this? Primarily, by following links (which is why internal links are so important for SEO). Because every link is a URL, URL structure is also critical for improving your site’s crawlability and rankings.
This is yet another reason to ensure that your URLs are simple, relevant, well organized, reader-friendly, and consistently reflect your site’s overall structure.
Using Software To Help With URL Structure Optimization
When it comes to URL structure optimization, Screaming Frog is the best platform for the job, in my opinion. Screaming Frog’s spider tool will crawl your website (just like a Google bot) and provide you with actionable insights on your website’s URL structure, length, and hierarchy.
Technical SEO
The lines between technical and on-page SEO are blurred, because many technical elements directly impact on-page elements and vice versa. Some SEO professionals see technical SEO as an entity unto itself, while others see it as a subset of on-page SEO. Semantics aside, the take-home message here is that you’ve got to consider technical SEO in your on-page strategy, or risk jeopardizing your rankings.
Here’s a brief list of technical SEO factors that can drastically improve your website’s SEO, but are not directly content related:
Technical SEO Factors
The Impact of Page Speed on On-Page SEO
I already touched on the importance of page speed for SEO in the image optimization section (above). But did you know that many website elements other than images can also slow down page speed? These include the quantity and type of files on a page, server response time, plugins, PC cache, traffic volume, and many more. It’s important to pay attention to all of them.
Optimizing Core Web Vitals & Using Lighthouse Reports
Core Web Vitals are metrics related to page speed and user interaction that Google considers important for user experience. You can check your website’s core web vitals using Google Search Console. Google Chrome’s Lighthouse is another fundamental tool that can help you effectively audit your website to optimize its speed and overall performance.
Structured Data (JSON-LD Schema)
Structured data is a standardized code format that’s used to make information on your website more readily understandable for search engines. It’s often optimized for rich snippets. JSON-LD Schema is one of the most lightweight and popular data formats for structured data.
Sitemaps
A sitemap is essentially a blueprint of your website that can be submitted to search engines. It’s a file that details the connections between all the pages and media on your website.
robots.txt and .htaccess
Robot.txt files control search engine crawler access to specific URLs on your website while .htaccess files are used to configure server settings.
SSL
A secure socket layer (SSL) is a security technology that keeps information private when passed between devices over the internet. SSL technology can give a boost to your site’s overall SEO performance.
HTTP Vs. HTTPS
HTTPS is the more secure version of HTTP and is therefore preferred by Google. Ensure your URLs begin with HTTPS to increase your site’s rankings.
Open Graph Tags & Twitter Cards
Open Graph Tags and Twitter Cards are both HTML tags containing data that communicates what should be displayed when a link to a specific page is shared on social media platforms. They’re important for SEO because they can drive traffic to your website.
Caching & Using a CDN
Caching is a method of speeding up your website’s loading time by temporarily storing files so that they can be accessed quickly by users. Using a content delivery network (CDN) to cache your website’s content can improve user experience by increasing your website’s speed.
Server-Side Optimization
Along with improving your website’s own speed, you can also use server-side optimization techniques to improve server performance.
4xx or 5xx Errors
4xx and 5xx errors should be avoided at all costs. Of course, they happen to the best of us. But it’s important to stay vigilant and deal with them as you become aware of them.
Canonicals
Canonical tags communicate to Google which version of a specific page you want to appear in search results. They’re especially important for avoiding duplicate content issues.
Compression Like GZIP or Brotli
GZIP and Brotli are both file compression software that can help increase the speed of your website. Remember, the smaller files are, the more quickly they’ll load.
Software To Help With Technical SEO
As I mentioned earlier, not all of the technical topics in the list above are traditionally part of on-page SEO. That being said, technical SEO and on-page SEO truly go hand in hand, so it’s paramount to mention them in this ultimate on-page guide.
As far as technical SEO tools are concerned, Screaming Frog is head and shoulders above the rest, in my opinion. For more in-depth information, check out my full Screaming Frog review.
Mobile Optimization
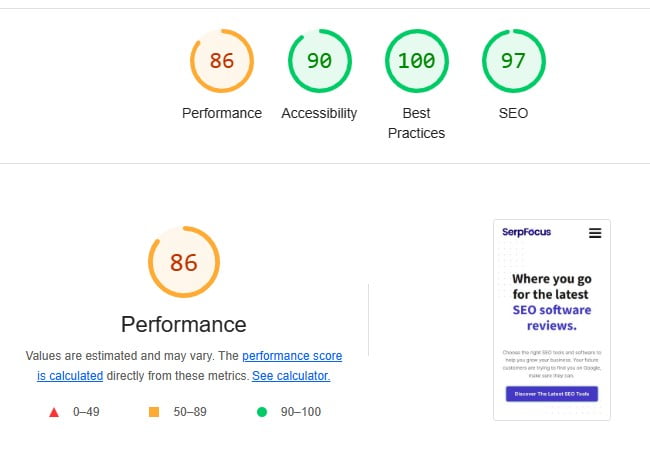
Mobile friendliness is defined as how effectively your website performs on mobile devices and is impacted by factors such as design, formatting, and responsiveness (which I’ll discuss in more detail below). Mobile friendliness is important for on-page SEO because, to put it bluntly, users avoid pages that don’t perform well on their mobile devices. Considering that more than 60% of online searches now take place on mobile devices, its significance truly cannot be overstated.
Basic tips for making your website mobile friendly include:
- Responsive design (see below)
- Streamlined content
- Compressing file sizes as much as possible
- Large/readable font
- Getting rid of pop-ups
As your website evolves, it’s important to check and optimize its mobile friendliness continually. Access your website on your own mobile device to get first-hand experience as a user, plus take advantage of some of the many tools that exist to help with mobile optimization. Google Search Console’s Mobile-Friendly test is a great starting point, but there are also many other dedicated platforms, such as mobiReady (which is free) or Pingdom.
Responsive Design
Responsive design describes the process of designing websites that automatically adapt to the parameters of the screen or device they are viewed on. Instead of just being a tinier (and more frustrating) version of a desktop site, a mobile responsive website is specifically designed to be accessed on various mobile devices.
While there are plenty of mobile responsive website templates available through different sources, designing a responsive website from the ground up is also an option. For more in-depth information about responsive design, check out Bootstrap, a website-building platform that’s been specifically engineered to support the process of creating responsive websites.
Google's Mobile-First Indexing
Today, Google predominantly uses websites’ mobile versions when indexing (and determining relevance and authority), which is a departure from the desktop-centric approach of the past. What this means for on-page SEO is that the mobile version of your website needs to be every bit as optimized and high-quality as your desktop version (potentially more so). Under no circumstances should you view your site’s mobile version as secondary.
On-Page SEO for E-Commerce Websites
Alongside all of the on-page elements covered so far, on-page SEO, specifically for e-commerce websites comes with its own unique set of challenges and opportunities.
Because e-commerce sites have so many pages (category pages, product pages, and more), their structure and optimization need to be crystal clear, and there’s not a lot of room for error. Think about it. If your URL structure is a mess on a small website with a few pages, it’s relatively easy to tackle. But on an e-commerce website with thousands of pages? That’s a different story.
On the other hand, e-commerce websites offer lots of opportunities for ranking in unique niches and engaging users in creative ways.
Here are a few tips to keep in mind when optimizing e-commerce pages:
- Remember to consider buyer intent and your sales funnel when researching keywords.
- Focus on optimizing product descriptions and images.
- Reviews are incredibly important! Use reputation management software to help elicit, sort through, and respond to product reviews.
- Use schema markups to produce rich snippets for your products.
- Be very vigilant about optimizing image sizes. E-commerce websites tend to have an enormous amount of images, which can impact page speed.
On-Page SEO for Local Business Websites
Local SEO is SEO that is focused on attracting customers within a particular geographical area and helping businesses appear in local search engine results for that area. Examples of businesses that rely heavily on local SEO include restaurants and food services, trades (plumber, electrician, etc.), real estate agencies, law firms, medical services, and more.
When optimizing local business websites for search engines, there are a few key strategies to keep in mind that differ slightly from broader on-page approaches:
- Location, location, location - A lot of what defines local SEO is its emphasis on location. In addition to geotagging images (which I covered earlier), here are a few more best practices:
- Embed your Google Business Profile map into the footer of your website to promote easy navigation.
- Use geo-modified keywords in title tags, meta descriptions, and more (e.g., Ashland plumber).
- Consider adding location pages to your website.
- Build relationships within your local community on social media and in person. Yes, it can actually positively impact your SEO.
- GMB - Make absolutely sure that you have fully optimized your GMB profile as well as updated your business’s listing in any other local directories.
- Rich Snippets - Use schema markup to increase your chances of getting rich snippets for your business.
- Manage reviews - This is a biggie. Elicit reviews, respond to them, and use them to your advantage. Aggregate review schema can encourage Google to feature your star rating, which can increase organic traffic and sales.
Using Plugins To Help With On-Page SEO on WordPress
If you’re still with me here, you’re undoubtedly realizing that a lot is encompassed within on-page SEO. While it’s important to wrap your head around the fundamentals of on-page SEO for your business, by no means will you have to slave over every miniscule detail of SEO for your website without any assistance. I don’t even think that’s possible.
That’s why SEO tools and plugins exist.
But if you’re just beginning the on-page optimization journey for your WordPress website, you may feel overwhelmed by the plethora of SEO plugins available.
Not sure where to start? Let me help by recommending two of my favorites:
Using Rank Math for On-Page SEO
In recent years, Rank Math has become my go-to on-page SEO plugin of choice. It’s super user-friendly and has a ton of features that can help you with all of the on-page elements I’ve covered in this guide, plus more. Here’s my full Rank Math review.
Using Yoast for On-Page SEO
Yoast is the original SEO plugin and still holds its own in today’s competitive market. Here’s my full Yoast review. **Insert link here.
Analyzing & Tracking Performance
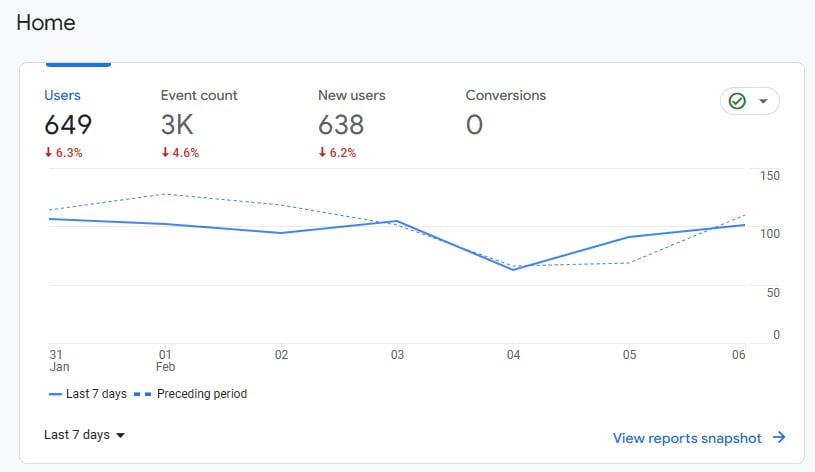
No matter how confident you are in your on-page SEO strategy, you’ll still want to track your website’s SEO performance over time. Without accurate data, it’s virtually impossible to move forward and grow your business in meaningful ways.
As I wrap up this on-page guide, I’d like to leave you with a few tips for successfully using analytics and tracking tools to measure your SEO success:
- Don’t get too stuck on keyword rankings alone - Keyword rankings are the obvious starting point (here’s my recent review of Keyword.com), but they don’t tell the whole story. You’ve also got to consider all the behind-the-scenes factors that impact them.
- Track Your Traffic - Use analytics to track where your organic traffic is coming from and how users are interacting with your site. Tweak your SEO strategy accordingly.
- Target Conversion Goals - Know what percentage of your organic traffic you want to be converting to paying customers. Assess your success regularly and note how different SEO strategies impact conversion rates.
These three tips are broad, overarching guidelines for tracking website performance, but they all rely on access to detailed and accurate data. Most SEO software includes data analysis features. That being said, if you’re looking for free and reliable metrics, Google Analytics and Google Search Console are always excellent starting points (as is Bing Webmaster Tools).
For specific SEO and digital marketing software reviews, please browse through the SerpFocus Reviews section, which provides honest reviews of some of my favorite SEO tools—including for analytics and performance tracking.
Conclusion
Has this post inspired you to dive deeper into on-page SEO strategies for your website? If the answer is yes, here’s the perfect tool: My personal on-page SEO checklist, ready for you to start using immediately. Download the SerpFocus On-Page SEO Checklist now!



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.