In the ever-evolving quest for perfect search engine optimization (SEO), there's no magic formula for rocketing your website to the coveted number one SERP spot. The first step is to understand the primary goal of a search engine and then leveraging that for your ranking benefits. Myriad factors and strategies work in combination with each other to determine a page's rank, and new ones are forever emerging. What worked flawlessly yesterday might need to be adjusted today. And that is just the reality of the SEO landscape.
If you're going to traverse this landscape with success, you'd best get comfortable with researching, tweaking, and taking risks from time to time. You should also learn to scrutinize the tactics that reflect Google's perpetually shifting crusade: Refining its capacity to understand search queries and delivering high-quality results in return.
Investing time in discerning the underpinnings of Google's increasingly advanced language processing capabilities is critical. Natural language processing represents the present and future of search engine optimization and you're not going to become (or remain) an SEO frontrunner without understanding it well enough to use it to your advantage.
At this point in time, that means getting a grasp on Google entities, among other things.
This article is closely tied to my recent article on finding NLP keywords for SEO, but here we'll focus more strategically on how to specifically leverage entities to improve your Google rankings. We'll define entities, review the basics of semantic SEO and Google's natural language processor (NLP), clarify the differences between content gap analysis and entity gap analysis, explore how Google scores for factors like salience and sentiment, and ultimately empower you to start creating content that’s high-quality and authoritative in your chosen niche.
Let's get started!
What Are Entities?
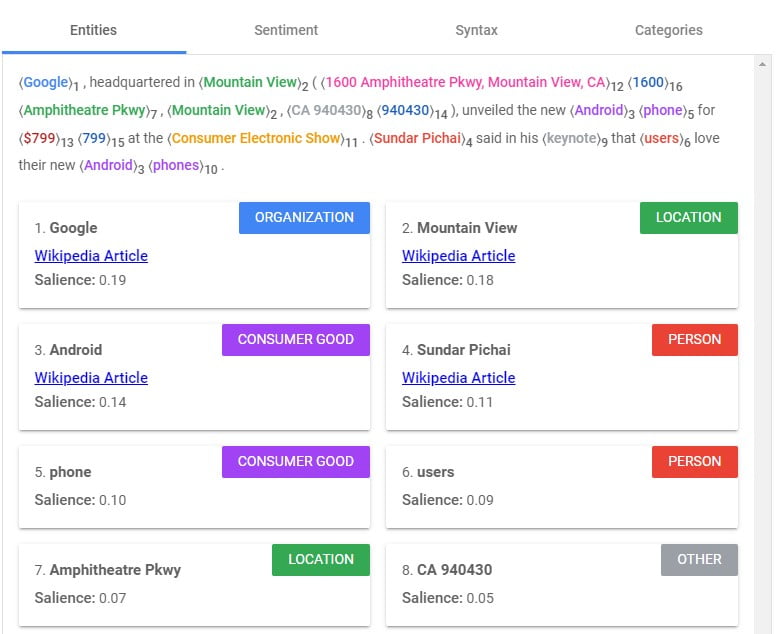
As defined by Google, an SEO entity is a thing or concept that is "singular, unique, well-defined, and distinguishable."
Huh?
That basically describes any one of billions of things in the entire universe.
But when you think about it, that's exactly the point of Google: To help people sift through billions of things in the universe to find pertinent, high-quality information about the one specific thing they’re seeking information about.
The smarter Google is about figuring out what a user is seeking (the search intent behind their query), the more satisfied that user will be. (And the more success Google will have.)
But Google users these days expect a lot. Gone are the days when people were ok with clunky keyword research that took some navigating. Today, users type complex queries into the Google search bar and expect precise, high-quality results in return...in milliseconds.
To keep up with such rigorous demands, Google has got to understand natural human language—the whole kit and kaboodle. Syntax, sentiment, expressions, connections, typos, and much more. Google's NLP capabilities are already pretty astonishing and constantly improving.
And that's where entities come into play. Unlike a keyword, an entity doesn't need to be a physical object or a specific word or phrase. Instead, an entity is connected to many different identifiers and can be defined by broader clues rather than narrow terms.
Google builds what’s known as a knowledge graph to improve its understanding of entities and to ultimately discover what a search query is intending to discover. The knowledge graph connects entities with their identifiers in an almost endless matrix (but keep in mind that each identifier can also be an entity in and of itself, connected to other identifiers that are also entities in and of themselves—so the knowledge graph is really a complex knowledge web connecting millions of entities).
For the entity "Disneyland", Google's knowledge graph may include identifiers (which may also be entities in their own right) such as "Walt Disney", "California", "family vacation", titles of movies, names of actors, specific rides, hotel prices, information about other Disney attractions, the history of Anaheim, reviews, contact information, hours, directions, highlights, and much, much, more.
Here’s an example of a tiny segment of the Google knowledge graph.
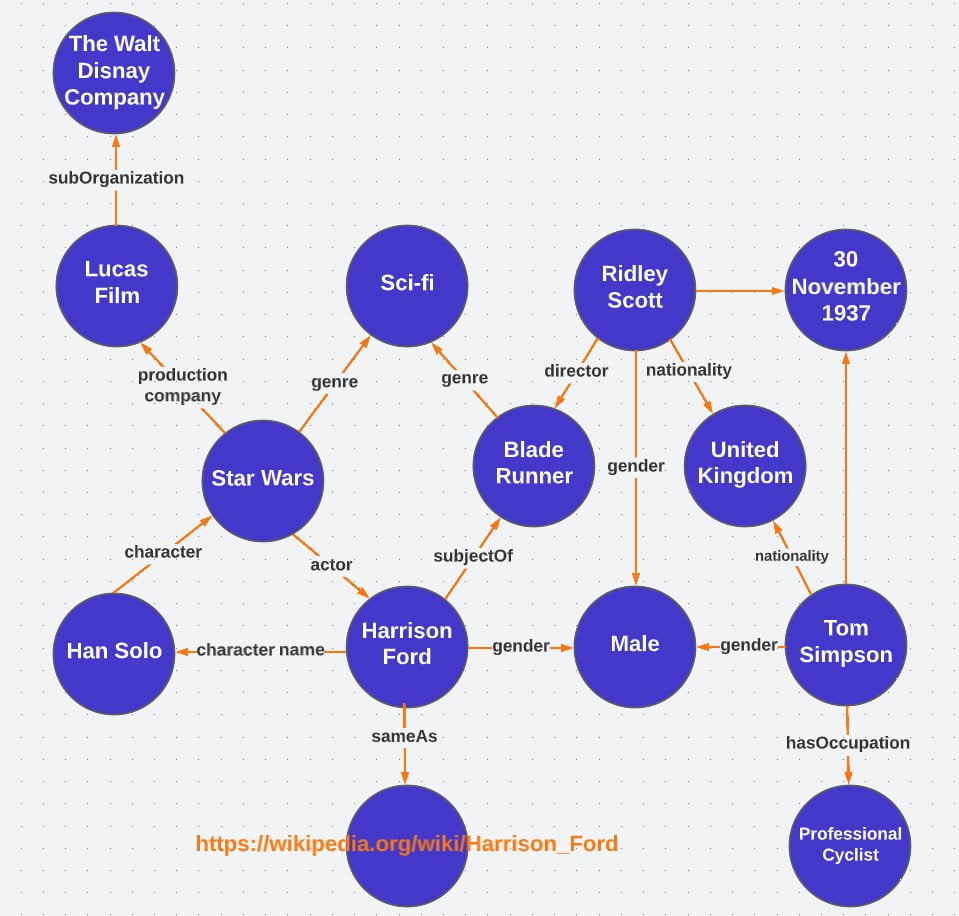
Entities are less ambiguous than keywords; they transcend language barriers and are contextually based. Ultimately, they’re an essential element of Google's natural language processing that greatly improves its algorithms' ability to understand the intent behind search queries and quickly return relevant results.
What Is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is search engine optimization that builds more meaning into content. Aside from increasing your site's overall quality (and, thus, ranking potential), semantic SEO grooms your site's content to be better understood by Google's crawlers.
Put another way—semantic SEO just adds yet another dimension to the content optimization you’re already focusing on for your web pages. For the purposes of this article, let's think about it centering around entity analysis rather than keyword analysis.
Google's Natural Language Processor & SEO
Hopefully, I've already made it clear that Google's natural language processor (NLP) is a core factor in how Google ranks content. If it's not already on your radar, now’s the time to make it a fundamental element of your SEO strategy. Pages that are optimized for entities will appear higher in organic search results, while those that aren’t may perform poorly.
Taking advantage of content strategy that foregrounds relevant entities is an impactful method for improving your rankings and the organic traffic flow to your website.
But how do you make that happen? The answer involves entity gap analysis. You'd be forgiven for wondering if that's the same thing as content gap analysis, but the truth is that they're related but different. Let's examine the two processes in a little more detail:
Content Gap Analysis Vs. Entity Gap Analysis
Content gap analysis is the process of finding holes in your existing content—pages that your website is missing. It involves comparing your website to your competitors' websites and identifying missing pages or content pieces that could improve your rankings and increase your organic traffic and revenue. Examples of content gaps might include blog posts that cover certain topics, service pages, the About page, or a Contact Page, to name a few.
Entity analysis also involves running a side-by-side comparison of your website and its search competitors. But instead of focusing on missing pages and elements, entity analysis helps you discover topics that are missing from within your page content itself.
Wouldn't it be phenomenal if there were a tool that could highlight the critical entity content that would bolster your rankings? Well, guess what? There is! And once again, it involves competitive analysis.
You can run a competitor's content directly through the Google NLP API, and it will pull out all of the entities that Google recognizes. With golden nuggets in hand, you can get to work optimizing your own content with these entities (and potentially more once you have a firm grasp on them and their relevant identifiers). These are your richest content opportunities!
Salience of Entities
Beyond simply including relevant entities in your content is the way these entities are used. Google's NLP aims to interpret entities in context and, from there, draws conclusions about your content—and how to rank it.
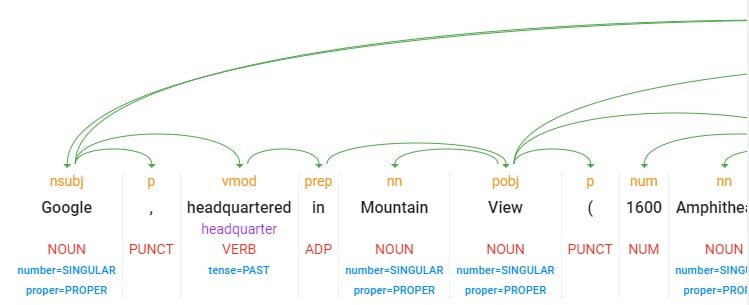
One way that Google scores entities in your content is by salience. In other words, the algorithm gives weight to entities based on how central it thinks they are to your content. It probably goes without saying, but this is important because you want Google to recognize the main entity in your content as having the highest salience (not some distantly related topic).
If your salience scores are not balancing out the way you'd hoped, sometimes a simple fix is just to reorganize your content so that your primary entity is mentioned first. Saliency analysis is recorded numerically by Google. It ranges from 0.0 for no saliency up to 1.0 for high saliency.
Sentiment of Content
Like salience, the sentiment of content is important. It plays a role in how your content is interpreted by Google's algorithms. If the sentiment of content in the niche you're trying to capture is overwhelmingly positive, then you'll want your content to reflect positivity as well. For instance, if the content in the top 10 SERPs for a term like "iPhone review" all have a positive sentiment toward the product, then ranking an article above them with negative sentiment will be nearly impossible because it will go against the grain of the group mentality.
While sentiment plays a role in any competitive analysis, you'll want to pay particular attention to content that involves opinions—like reviews or debates.
The Google algorithm scores texts to determine whether they’re positive, negative, or neutral. Positive sentiment is scored between 0.25 and 1, while negative sentiment is given a value between -0.25 and -1. Neutral sentiment falls in the numerical range between -0.25 and 0.25.
Categories & Confidence
In addition to salience and sentiment, Google's NLP also categorizes content and gives it a score for confidence. While categories are something we're pretty familiar with in the SEO trenches, the confidence score may throw us off at first, so let's take a slightly more in-depth peek.
Google's confidence score represents Google's confidence that it has returned a relevant result for the search query entered. Jason Barnard sums it up well when he explains that the score is based off of a combination of multiple confidence measurements that include: "it's understanding of the entity returned; it's confidence that the input query is a pseudonym for the entity returned; and the perceived strength of the relationship between the entity Google has recognized from the input query and the entity returned".
If you write content and the category comes back totally wrong, you'll want to consider adding more entities surrounding your main topic to build Google's confidence.

Become an Authority
In the end, it all boils down to creating authoritative content. To become an authority in your niche (at least according to Google), include as many relevant entities as you can in your content.
Entity-based SEO can make the difference between high-quality content and high-quality content that’s recognized by Google's algorithms. Get the formula right, and claim the high search results you deserve!
Summing It Up
Using entity gap analysis in your SEO strategy just makes good sense. Getting familiar with Google's natural language processor will allow you to start harnessing its power to your advantage. Semantic SEO is (at least part of) the The Future Of SEO & How To Stay Ahead Of The Curve">future SEO landscape, so you're going to have to dive in sooner or later.
I recommend sooner...and I'm here to help you along the way if you need it!
SerpFocus Consulting
Whether you're an SEO newbie or a seasoned professional, there will always be times when you have questions about how best to optimize your own business for search engines.
SEO can be a wild ride, and my goal with SerpFocus is to provide SEO consulting along the way. With years of industry experience, I'd be delighted to lend a discerning eye to your specific goals and methodology and teach you some valuable skills while we’re at it.
If you've got burning questions about Semantic SEO, NLP keywords, entity gap analysis, or any other SEO-related topics, reach out to me at SerpFocus today!



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.